Abstract
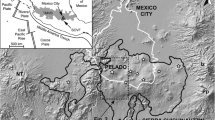
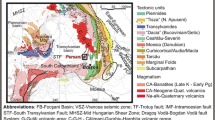
Late Holocene volcanic activity at Ruapehu has been characterizedby the generation of small (<105 m3) to very large (>107 m3) lahars and repeated,small to medium (VEI 1-3) tephra-producing eruptions. The Onetapu Formation groupsall lahar deposits that accumulated during the last 2,000 years on the southeastern Ruapehu ring plain. The andesitic tephras are grouped within the Tufa Trig Formation and are intercalated within the laharic sequence. By correlating these two formations with new radiocarbon ages obtained on interbedded paleosols, we reconstruct a detailed volcanic history of Ruapehu for this period.
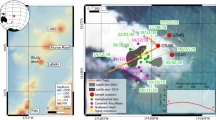
Clast assemblages identified in the laharic sequences record thelithologies of synchronous tephras and rocks within the source region. These assemblages suggest a strong genetic link between the development of Crater Lake, the variation in eruptivestyles, and the production of lahars.
Lahar-triggering mechanisms include: (1) flank collapse ofhydrothermally altered and unstable portions of the cone; (2) phreatic and phreatomagmatic eruptions favoring the generation of snow-rich slurries and hyperconcentrated stream flows; (3) suddenCrater Lake rim collapse, releasing large amounts of water inducing debris flows; and (4) eruptions that generate large volumes of tephra on snow-covered slopes, later remobilized by heavy rain.
Two major lahars in the Onetapu sequence had a volume≥ 4 × 107 m3, roughly 1 to 2 orders of magnitude larger than the 1953event leading to the Tangiwai disaster (151 casualties). One of these lahars crossed over a lowinterfluve currently separating the Whangaehu River from a stream feeding the Tongariro River,sometime since peat accumulated between AD 1400 and AD 1660. A repetition of such a large-scaleevent would have devastating consequences on the infrastructure, economy and environment withinthe distal areas of the two catchments. The 1995–1996 eruptions were a timely reminder ofthe hazards posed by the volcano.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell, I. B.: 1973, Recent aggradation in Whangaehu Valley, Central North Island, New Zealand, New Zealand J. Geol. Geophys. 16, 643–649.
Christenson, B. W. and Wood, C. P.: 1993, Evolution of a vent-hosted hydrothermal system beneath Ruapehu Crater Lake, New Zealand, Bull. Volcanol. 55, 547–565.
Cronin, S. J. and Neall, V. E.: 1997, A late Quaternary stratigraphic framework for the northeastern Ruapehu and eastern Tongariro ring plains, New Zealand, New Zealand J. Geol. and Geophys. 40, 185–197.
Cronin, S. J., Neall, V. E., Lecointre J. A., and Palmer, A. S.: 1996, Unusual “snow slurry” lahars from Ruapehu volcano, New Zealand, September 1995, Geology 24, 1107–1110.
Cronin, S. J., Neall, V. E., Lecointre, J. A., and Palmer, A. S.: 1997a, Changes in Whangaehu river lahar characteristics during the 1995 eruption sequence, Ruapehu volcano, New Zealand, J. Volcanol. and Geotherm. Res 76, 47–61.
Cronin, S. J., Hodgson, K. A., Neall, V. E., Palmer, A. S. and Lecointre, J. A.: 1997b, 1995 Ruapehu lahars in relation to the late Holocene lahars of Whangaehu River, New Zealand, New Zealand J. Geol. and Geophys. 40, 507–520.
Cronin, S. J., Hedley, M. J., Neall, V. E., and Smith, R. G.: 1998, Agronomic impact of tephra fallout from the 1995 and 1996 Ruapehu Volcano eruptions, New Zealand, Environ. Geol. 34, 21–30.
Cronin, S. J., Lecointre, J. A., Palmer, A. S., and Neall, V. E.: 2000, Transformation, stratification, and deposition of a channelised, multiple-peaked lahar flow, New Zealand J. Geol. and Geophys. 43, 117–128.
Donoghue, S. L.: 1991, Late Quaternary volcanic stratigraphy of the southeastern sector of the Mount Ruapehu ring plain, New Zealand, unpublished PhD thesis, Massey University, New Zealand.
Donoghue, S. L. and Neall, V. E.: 2001, Late Quaternary constructional history of the southeastern Ruapehu ring plain, New Zealand, New Zealand J. Geol. and Geophys. 44, 439–466.
Donoghue, S. L., Neall, V. E., and Palmer, A. S.: 1995, Stratigraphy and chronology of late Quaternary tephra deposits, Tongariro Volcanic Centre, New Zealand, J. Royal Soc. of New Zealand 25, 115–206.
Donoghue, S. L., Neall, V. E., Palmer, A. S., and Stewart, R. B.: 1997, The volcanic history of Ruapehu during the last 2 millennia based on the record of the Tufa Trig Tephras, Bull. Volcanol. 59, 136–146.
Healy, J., Lloyd, E. F., Rishworth, D. E. H., Wood, C. P., Glover, R. B., and Dibble, R. R.: 1978, The eruption of Ruapehu, New Zealand on 22 June 1969, New Zealand Dept. of Sci. and Ind. Res. Bull. 224, 80.
Hodgson, K. A.: 1993, Late Quaternary lahars from Mount Ruapehu in the Whangaehu River Valley, North Island, New Zealand, unpublished PhD thesis, Massey University, New Zealand.
Hodgson, K. A. and Manville, V. R.: 1999, Sedimentology and flow behavior of a rain-triggered lahar, Mangatoetoenui Stream, Ruapehu volcano, New Zealand, GSA Bull. 111, 743–754.
Houghton, B. F., Neall, V. E. and Johnston, D. M.: 1996, Eruption! Mount Ruapehu Awakes, Penguin Books (NZ), Auckland.
Johnston, D. M., Houghton, B. F., Neall, V. E., Ronan, K. R., and Paton, D.: 2000, Impacts of the 1945 and 1995–1996 Ruapehu eruptions, New Zealand: An example of increasing societal vulnerability, GSA Bull. 112, 720–726.
Keys, H.: 1999, Ruapehu Crater Lake issue, Tongariro, the Annual. Department of Conservation Report 8, 49–51.
Keys, H.: 2001, Scoping the Alarm and Warning System for Ruapehu Lahars in Whangaehu and Tongariro Catchments, Department of Conservation Report TONCO-17290, Turangi.
Lecointre, J. A., Neall, V. E., and Palmer, A. S.: 1998, Quaternary lahar stratigraphy of the western Ruapehu ring plain, New Zealand, New Zealand J. Geol. Geophys. 41, 225–245.
Lecointre, J. A., Neall, V. E., and Hodgson, K. A.: 1999, Onetapu Lahars are a key to understanding the history of Crater Lake, Ruapehu, 2,000 14C years to the present, Geol. Soc. of New Zealand Misc. Publication 107A, 84.
Lecointre, J. A., Neall, V. E., Wallace, R. C., and Prebble, W. R.: 2002, The 55–60 ka Te Whaiau Formation: A catastrophic, avalanche-induced, cohesive debris flow from Proto-Tongariro Volcano, New Zealand, Bull. Volcanol. 63, 509–525.
Manville, V., Hodgson, K. A., Houghton, B. F., Keys, J. R., and White, J. D.: 2000, Tephra, snow and water: Complex sedimentary responses at an active snow-capped stratovolcano, Ruapehu, New Zealand, Bull. Volcanol. 62, 278–293.
McPhie, J., Doyle, M., and Allen, R.: 1993, Volcanic Textures — A Guide to the Interpretation of Textures in Volcanic Rocks, CODES Key Centre, University of Tasmania, Hobart.
Nairn, I. A., Wood, C. P., and Hewson, C. A. Y.: 1979, Phreatic eruptions of Ruapehu: April 1975, New Zealand J. Geol. and Geophys. 22, 155–173.
Neall, V., Lecointre, J., and Hodgson, K.: 1999a, Towards understanding lahar-triggering mechanisms at Ruapehu, Proc. IUGG'99 General Assembly, Symposium JSP23, Birmingham, UK.
Neall, V. E., Houghton, B. F., Cronin, S. J., Donoghue, S. L., Hodgson, K. A., Johnston, D. M., Lecointre, J. A., and Mitchell, A. R.: 1999b, Volcanic hazards at Ruapehu. Ministry of Civil Defence, Wellington, Volcanic Hazards Information Series 8, 1–30.
O'Shea, B. E.: 1954, Ruapehu and the Tangiwai disaster, New Zealand J. Sci. and Tech. B36, 174–189.
Otway, P. M., Hodgson, K. A., and Nairn, I. A.: 1995, Whakapapa Skifields Lahar Study, Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences Science Report 95/39, Wellington.
Palmer, B. A., Purves, A. M., and Donoghue, S. L.: 1993, Controls on accumulation of a volcaniclastic fan, Ruapehu composite volcano, New Zealand, Bull. Volcanol. 55, 176–189.
Paterson, B. R., Page, C. E., and Cudby, E. J.: 1976, The Effects of Lahars from the 1975 April Mount Ruapehu Eruption and the Threat of Future Eruptions on Tongariro Power Development, Unpublished New Zealand Geol. Surv. Geology Rep. EG 230.
Pierson, T. C. and Costa, J. E.: 1987, A rheologic classification of subaerial sediment-water flows, Geol. Soc. Am. Rev. Engin. Geol. VII, 1–12.
Purves, A.M.: 1990, Landscape Ecology of the Rangipo Desert, unpublished Masters thesis, Massey University, New Zealand.
Ruapehu Surveillance Group: 1996, Volcanic eruption at a New Zealand ski resort prompts reevaluation of hazards, Eos, Transactions, American Geophysical Union 77, 189–191.
Smith, G. A. and Fritz, W. J.: 1989, Volcanic influences on terrestrial sedimentation, Geology 17, 375–376.
Vallance, J. W.: 2000, Lahars, in H. Sigurdsson, B. Houghton, S. R. McNutt, H. Rymer, and J. Styx (eds.), Encyclopedia of Volcanoes, Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 601–616.
Vallance, J. W. and Scott, K. M.: 1997, The Osceola mudflow from Mount Rainier: Sedimentology and hazard implications of a huge clay-rich debris flow, Geol. Soc Am. Bull. 109, 143–163.
Yamagishi, H.: 1987, Studies on the Neogene subaqueous lavas and hyaloclastites in southwest Hokkaido, Rep. Geol. Surv. Hokkaido 59, 55–117.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lecointre, J., Hodgson, K., Neall, V. et al. Lahar-Triggering Mechanisms and Hazard at Ruapehu Volcano, New Zealand. Natural Hazards 31, 85–109 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NHAZ.0000020256.16645.eb
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NHAZ.0000020256.16645.eb