Abstract
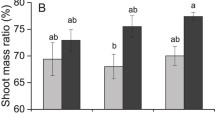
Sediment cores were collected from two of the Norfolk Broadsandtwo of the West Midland Meres, to test the hypothesis thatrootedmacrophytes increase the sediment release rate of phosphorusduringthe growing season.These were taken from inside and outside plant beds (mixedMyriophyllum spicatum and Chara sp. in Hickling BroadandNuphar lutea in Burntfen Broad, Mere Mere and LittleMere).The overlying water was replaced with a standard waterdesigned tomimic lowland freshwater. After an overnight ‘batch’incubation thewater was analysed for TP and SRP. From this their releaserateswere calculated. Interstitial measurements of SRP were alsomadefor some of the Broads cores at the end of the incubationperiod.The data were analysed using General Linear Models. TP and SRPwerethe responses for both data sets. Factors for the Broads wereinside/outside plant beds, date, and site, whilst for theMeres thefactors of date and site could not be delineated.Release rates in this study were affected by a number offactors(plants, site and date). The picture emerging so far is thatwhenrooted macrophytes have a significant effect on phosphorusreleasethey increase it. However the large variability betweenreplicateshighlights the logistical difficulties in running suchexperiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, J. M., 1982. Effect of nitrate concentration in lake water on phosphate release from the sediment. Wat. Res. 16: 1119–1126.
Bales, M., B. Moss, G. Phillips, K. Irvine & J. Stansfield, 1993. The changing ecosystem of a shallow, brackish lake, Hickling Broad, Norfolk, U.K. II. Long-term trends in water chemistry and ecology and their implications for restoration of the lake. Freshwat. Biol. 29: 141–165.
Carignan, R. & J. Kalff, 1980. Phosphorus sources for aquatic weeds: water or sediments? Science 207: 987–988.
Carpenter, S. R., 1981. Submerged vegetation: an internal factor in lake ecosystem succession. Am. Nat. 118: 372–383.
Carpenter, S. R., J. J. Elser & K. M. Olson, 1983. Effects of roots of Myriophyllum verticillatumL. on sediment redox conditions. Aquat. Bot. 17: 243–249.
Denny, P., 1972. Sites of nutrient absorption in aquatic macrophytes. J. Ecol. 60: 819–829.
Driscoll, C. T., 1993. Supply of phosphorus to the water column of a productive hardwater lake: controlling mechanisms and management considerations. Hydrobiologia 253: 61–72.
Gambrell, R. P. & W. H. Patrick Jr., 1978. Chemical and microbiological properties of anaerobic soils and sediments. In Hook, D. D. and R. M. M. Crawford (eds), Plant Life in Anaerobic Environments. Ann Arbor Science: 375–423.
Holdway, P. A., R. A. Watson & B. Moss, 1978. Aspects of the ecology of Prymnesium parvum(Haptophyta) and water chemistry of the Norfolk Broads, England. Freshwat. Biol. 8: 295–311.
Jensen, H. S. & F. O. Andersen, 1992. Importance of temperature, nitrate, and pH for phosphate release from aerobic sediments of four shallow, eutrophic lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 37: 577–589.
Jeppesen, E., P. Kristensen, J. P. Jensen, M. Sondergaard, E. Mortensen & T. Lauridsen, 1991. Recovery resilience following a reduction in external phosphorus loading of shallow, eutrophic Danish lakes: duration, regulating factors and methods for overcoming resilience. Mem. Ins. ital. Idrobiol. 48: 127–148.
John, M. K., 1970. Colorimetric determination of phosphorus in soil and plant materials with ascorbic acid. Soil Science 4: 214–220.
Kairesalo, T. & T. Matilainen, 1994. Phosphorus fluctuation in water and deposition into sediment within an emergent macrophyte stand. Hydrobiologia. 275/276: 285–292.
Marsden, M. W., 1989. Lake restoration by reducing external phosphorus loading: the influence of sediment phosphorus release. Freshwat. Biol. 21: 139–162.
Mortimer, C. H., 1941. The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes. J. Ecol. 29: 280–329.
Mortimer, C. H., 1942. The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes. J. Ecol. 30: 147–201.
Moss, B., 1987. The Broads. Biologist 34: 7–13.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analyt. chim. Acta 27: 31–36.
Otsuki, A. & R. G. Wetzel, 1972. Coprecipitation of phosphate with carbonates in a marl lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17: 763–767.
Phillips, G., R. Jackson, C. Bennett & A. Chilvers, 1994. The importance of sediment phosphorus release in the restoration of very shallow lakes (The Norfolk Broads, England) and implications for biomanipulation. Hydrobiologia. 275/276: 445–456.
Pitt, J.-A., 1994. Phosphorus release and sediment chemistry. In Pitt, J.-A. & G. L. Phillips (eds), The Development of Biomanipulation Techniques and Control of Phosphorus Release from Sediments. National Rivers Authority Report Number 475/2/A: 19–61.
Rorslett, B., D. Berge & S. W. Johansen, 1985. Mass invasion of Elodea canadensisin a mesotrophic, South Norwegian lake-impact on water quality. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 22: 2920–2926.
Serruya, C., M. Edelstein, U. Pollingher & S. Serruya, 1974. Lake Kinneret sediments: Nutrient composition of the pore water and mud exchanges. Limnol. Oceanogr. 19: 489–508.
Sondergaard, M., P. Kristensen & E. Jeppesen, 1993. Eight years of internal phosphorus loading and changes in the sediment phosphorus profile of Lake Sobygaard, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 253: 345–356.
Stephens, K., 1963. Determination of low phosphate concentrations in lake and marine waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 8: 361–362.
Wium-Andersen, S. & J. M. Andersen, 1972. The influence of vegetation on the redox profile of the sediment of Grane Langso, a Danish Lobelialake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17: 948–952.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stephen, D., Moss, B. & Phillips, G. Do rooted macrophytes increase sediment phosphorus release?. Hydrobiologia 342, 27–34 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017019713123
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017019713123