Abstract
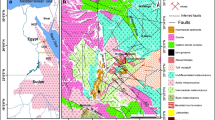
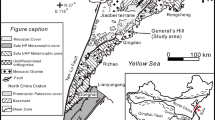
Tertiary subvolcanic basic rocks are found as sills, dykes, and stocks in the southern flanks of the Central Alborz Magmatic Belt, north of Tehran. The rocks can be divided into two subvolcanic rock groups based on their geographic locations: (1) the western Kiga group and (2) an eastern group. The eastern group range from micromonzogabbro/diorite to microgabbro, whereas the Kiga group consists of micromozodiorite to micromonzogabbro. Mineral compositions, whole-rock major and trace elements show that these rocks have calc-alkaline affinities. The eastern group extends to higher MgO (4–10wt%) than the Kiga group (MgO= 4–5 wt%). With decreasing MgO, the contents of SiO2, TiO2, Al2O3, Na2O, and P2O5 increase and the contents of CaO and compatible trace elements (e.g., Co, Ni, Cr) decrease, consistent with olivine and clinopyroxene fractionation. At a given MgO, the Kiga rocks have higher FeOt, K2O, and P2O5 and extend to higher overall highly to moderately incompatible elements (Rb, Ba, Th, U, Nb, Ta, LREE, Sr, and Zr) and lower Al2O3 and Na2O. The depletion in Nb and Ta but enrichments in Rb, Ba, Th, U, K, Pb, and Sr, compared to N-MORB as well as high Th/Yb (at a given Nb/Yb or Ta/Yb), indicates a subduction zone origin for both subvolcanic groups of rocks. The initial Sr and Nd isotopic ratios of the subvolcanic rocks vary from 0.7048 to 0.7064 and 0.5126 to 0.5128, respectively. Furthermore, εNd (50 Ma) values (+0.64 to +5.19) associated with the two-stage model ages (0.42 to 0.78 Ga) of the samples infer a contribution of Cadomian-enriched lithospheric mantle in their source for this melt. The most evolved sample from the Kiga group has the lowest 143Nd/144Nd and highest 206Pb/204Pb and 208Pb/204Pb ratios. The isotope correlations could be explained by upper crustal assimilation/contamination by the more evolved samples or reflect source differences (i.e., higher amount of subducted sediments) in the Kiga source. In conclusion, we interpret that the subvolcanic rocks have formed in an active continental margin.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Representative data are available in the manuscript. All data will be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abbassi N, Lockley MG (2004) Eocene bird and mammal tracks from the Karaj Formation, Tarom Mountains, northwestern Iran. Ichnos 11(3–4):349–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/10420940490428689
Agard P, Omrani J, Jolivet L, Mouthereau F (2005) Convergence history across Zagros (Iran): constraints from collisional and earlier deformation. Int J Earth Sci 94(3):401–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-005-0481-4
Aghanabati A (2006) Geology of Iran. Geol Surv Iran and Mineral Exploration, Tehran, p 586
Alavi M (1994) Tectonics of the Zagros orogenic belt of Iran: new data and interpretations. Tectonophysics 229(3–4):211–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(94)90030-2
Allegre CJ, Minster JF (1978) Quantitative models of trace element behavior in magmatic processes. Earth and Planet Sci Lett 38(1–25):1. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821X(78)90123-1
Allen MB, Armstrong HA (2008) Arabia-Eurasia collision and the forcing of mid-Cenozoic global cooling. Palaeogeog Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 265:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.04.021
Allen MB, Ghassemi MR, Shahrabi M, Qorashi M (2003) Accommodation of late Cenozoic oblique shortening in the Alborz range, northern Iran. J Structural Geol 25(5):659–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8141(02)00064-0
Amini M, Emami A (1993) Geological map of Tehran (1: 100,000 scale). Geolo Surv Iran, Tehran
Aparicio A (2010) Relationship between clinopyroxene composition and the formation environment of volcanic host rocks. IUP J of Earth Sci.
Asiabanha A, Foden J (2012) Post-collisional transition from an extensional volcano-sedimentary basin to a continental arc in the Alborz Ranges, N-Iran. Lithos 148:98–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2012.05.014
Axen GJ, Lam PS, Grove M, Stockli DF, Hassanzadeh J (2001) Exhumation of the west-central Alborz Mountains, Iran, Caspian subsidence, and collision-related tectonics. Geology 29:559–562. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029%3c0559:EOTWCA%3e2.0.CO;2
Azizi H, Jahangiri A (2008) Cretaceous subduction-related volcanism in the northern Sanandaj-Sirjan Zone. Iran. J Geodyn 45:178–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2007.11.001
Ballato P, Uba CE, Landgraf A, Strecker MR, Sudo M, Stockli DF, Friedrich A, Tabatabaei SH (2011) Arabia-Eurasia continentalcollision: insights from late Tertiary foreland-basin evolution in the Alborz mountains, northern Iran. Geol Soc Am Bull 300:125–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2010.09.043
Bau M (1996) Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: evidence from Y/ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Contrib Mineral Petrol 123:323–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050159
Bau M, Dulski P, Moller P (1995) Yttrium and holmium in South Pacific seawater: vertical distribution and possible fractionation mechanisms. Chem Erde 55:1–15
Berberian F, Berberian M (1981) Tectono-Plutonic episodes in Iran. Geol Surv of Iran, Rep. 52:566–593
Brunet MF, Granath JW, Wilmsen M (2009) South Caspian to central Iran basins: introduction. Geolo Soc London Special Publications 312(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP312.1
Davidson J, Hassanzadeh J, Berzins R, Stockli DF, Bashukooh B, Turrin B, Pandamouz A (2004) The geology of Damavand volcano, Alborz Mountains, northern Iran. Geol Soc Am Bull 116(1–2):16–29. https://doi.org/10.1130/B25344.1
Deer WA, Howie RA, Zussman J (1992) An introduction to rock forming minerals. Harlow: Longman. 696 p. https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.1992.056.385.20.
De la Roche HD, Leterrier JT, Grandclaude P, Marcha M (1980) A classification of volcanic and plutonic rocks using R1–R2 diagram and major-element analyses—its relationships with current nomenclature. Chem Geol 29:183–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(80)90020-0
Dilek Y, Imamverdiyev N, Altunkaynak S (2010) Geochemistry and tectonics of Cenozoic volcanism in the Lesser Caucasus (Azerbaijan) and the peri-Arabian region: collision-induced mantle dynamics and its magmatic fingerprint. Int Geol Rev 52:536–578. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206810903360422
Dong Y, Xiao L, Zhou H, Du J, Zhang N, Xiang H, Wang C, Zhao Z, Huang H (2010) Volcanism of the Nanpu Sag in the Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China: geochemistry, petrogenesis, and implications for tectonic setting. J Asian Earth Sci 39(3):173–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.03.003
Ghorbani M (2013) A summary of geology of Iran. In: Ghorbani M (ed) The economic geology of Iran: mineral deposits and natural resources. Springer Geology. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 45–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5625-0_2
Ghorbani MR, Graham IT, Ghaderi M (2014) Oligocene-Miocene geodynamic evolution of the central part of Urumieh-Dokhtar Arc of Iran. Int Geol Rev 56:1039–1050. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2014.919615
Guest B, Stockli DF, Grove M, Axen GJ, Lam PS, Hassanzadeh J (2006) Thermal histories from the central Alborz Mountains, northern Iran: implications for the spatial and temporal distribution of deformation in northern Iran. Geol Soc Am Bull 118(11–12):1507–1521. https://doi.org/10.1130/B25819.1
Harker A (1909) The natural history of igneous rocks. Macmillam 384 p.
Hey MH (1954) A new review of the chlorites. Mineralogical Magazine and J of the Mineralogical Soc 30(224):277–292. https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.1954.030.224.01
Hoernle K, Tilton G (1991) Sr-Nd-Pb isotope data for Fuerteventura (Canary Islands) basal complex and subaerial volcanics: applications to magma genesis and evolution. Schweiz Mineral Petrogr Mitt 71:5–21. https://doi.org/10.5169/seals-54342
Homke S, Vergés J, Garcés M, Emami H, Karpuz R (2004) Magnetostratigraphy of Miocene-Pliocene Zagros foreland deposits in the front of the Push-e Kush arc (Lurestan Province, Iran). Earth Planet Sci Lett 225(3–4):397–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2004.07.002
Jamali H, Dilek Y, Daliran F, Yaghubpur A, Mehrabi B (2010) Metallogeny and tectonic evolution of the Cenozoic Ahar-Arasbaran volcanic belt, northern Iran. Int Geol Rev 52:608–630. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206810903416323
Jarosewich E (2002) Smithsonian microbeam standards. J Res Natl Inst Stand Technol 107:681–686. https://doi.org/10.6028/jres.107.054
Jarosewich E, Nelen JA, Norberg JA (1980) Reference samples for electron microprobe analysis. Geostand Newsl 4(1):43–47. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-908X.1980.tb00273.x
Jung D, Kursten M, Tarakian M (1976) Post-Mesozoic volcanism in Iran and its relation to the subduction of the Afro-Arabian under the Eurasian plate, in: Pilger, A, and Rosler, A (Eds.), Afar between continental and oceanic rifting. Stuttgart, Schweizerbatsche Verlagsbuch-handlung, 2: 175–181.
Kay SM, Coira BL, Caffe PJ, Chen CH (2010) Regional chemical diversity, crustal and mantle sources and evolution of central Andean Puna plateau ignimbrites. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 198(1–2):81–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2010.08.013
Kemner F, Haase KM, Beier C, Krumm S, Brandl PA (2015) Formation of andesite melts and Ca-rich plagioclase in the submarine Monowai volcanic system. Kermadec Arc. Geochem Geophy Geosy 16(12):4130–4152. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GC005884
Kheirkhah M, Allen MB, Emami M (2009) Quaternary syn-collision magmatism from the Iran/Turkey borderlands. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 182:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjvolgeores200901026
Kretz R (1983) Symbols for rock forming minerals. Am Mineral 68:277–279
Leterrier J, Maury RC, Thonon P, Girard D, Marchal M (1982) Clinopyroxene composition as a method of identification of the magmatic affinities of paleo-volcanic series. Earth Planet Sci Lett 59(1):139–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821X(82)90122-4
Liotard JM, Dautria JM, Bosch D, Condomines M, Mehdizadeh H, Ritz JF (2008) Origin of the absarokite–banakite association of the Damavand volcano (Iran): trace elements and Sr, Nd, Pb isotope constraints. Int J Earth Sci 97(1):89–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-006-0159-6
Maghdour-Mashhour R, Esmaeily D, Shabani AAT, Chiaradia M, Latypov R (2015) Petrology and geochemistry of the Karaj Dam basement sill: implications for geodynamic evolution of the Alborz magmatic belt. Chem Erde 75(2):237–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2015.03.001
McQuarrie N, Stock JM, Verdel C, Wernicke BP (2003) Cenozoic evolution of Neotethys and implications for the causes of plate motions. Geophys Res Lett 30(20). https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL017992.
Mirnejad H, Hassanzadeh J, Cousens BL, Taylor BE (2010) Geochemical evidence for deep mantle melting and lithospheric delamination as the origin of the inland Damavand volcanic rocks of northern Iran. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 198(3–4):288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2010.09.014
Moradi M, Basiri S, Kananian A, Kabiri K (2015) Fuzzy logic modeling for hydrothermal gold mineralization mapping using geochemical, geological, ASTER imageries and other geo-data, a case study in Central Alborz. Iran. Earth Sci Inform 8:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-014-0151-9
Morimoto N (1988) Nomenclature of pyroxenes. Can Mineral 27:143–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2012.09.052
Nabatian G, Ghaderi M, Neubauer F, Honarmand M, Liu X, Dong Y, Jiang S, Quadt A, Bernroider M (2014) Petrogenesis of Tarom high-potassic granitoids in the Alborz-Azarbaijan belt, Iran: geochemical, U-Pb zircon and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic constraints. Lithos 184:324–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2013.11.002
Namnabat E, Ghorbani M, Nakashima K, Tabatabaei SH, Tavakoli N (2021) Mineral chemistry and Petrology of the Andarian volcanic rocks: insight to the Ahar-Arasbaran magmatic zone, Northwestern Iran. Arab J Geosci 14:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08246-1
Neill I, Meliksetian K, Allen MB, Navasardyan G, Kuiper K (2015) Petrogenesis of mafic collision zone magmatism: The Armenian sector of the Turkish-Iranian Plateau. Chem Geol 403:24–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.03.013
Pearce JA (1982) Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries. In: Thorpe, RS. (Eds.), Andesites: Orogenic andesites and related rocks. J Wiley and Sons, pp: 525-548.
Pearce JA (2008) Geochemical fingerprinting of oceanic basalts with applications to ophiolite classification and the search for Archean oceanic crust. Lithos 100:14–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2007.06.016
Philip H, Cisternas A, Gvishiani A, Gorshkov A (1989) The Caucasus: an actual example of the initial stages of continental collision. Tectonophysics 161(1–2):1–21
Polat A, Hofmann AW (2003) Alteration and geochemical patterns in the greenstone belt 3.7–3.8 Ga Isua. West Greenland. Precambrian Res 126:197–2183. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-9268(03)00095-0
Putirka K, Johnson M, Kinzler R, Longhi J, Walker D (1996) Thermobarometry of mafic igneous rocks based on clinopyroxene-liquid equilibria, 0–30 kbar. Contrib to Mineral Petrol. 123:92–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050145
Rabiee A, Rossetti F, Asahara Y, Azizi H, Lucci F, Lustrino M, Nozaem R (2020) Long-lived, Eocene-Miocene stationary magmatism in NW Iran along a transform plate boundary. Gondwana Res 85:237–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2020.03.014
Rezaeian M, Carter A, Hovius N, Allen MB (2012) Cenozoic exhumation history of the Alborz Mountains, Iran: new constraints from low-temperature chronometry. Tectonics 31:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011TC002974
Robertson AH (2000) Mesozoic-Tertiary tectonic-sedimentary evolution of a south Tethyan oceanic basin and its margins in southern Turkey. Geol Soc, London, Special Publications 173:97–138. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL
Saccani E (2015) A new method of discriminating different types of post-Archean ophiolitic basalts and their tectonic significance using Th-Nb and Ce-Dy-Yb systematics. Geosci Front 6(4):481–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2014.03.006
Sokol K, Halama R, Meliksetian K, Savov IP, Navasardyan G, Sudo M (2018) Alkaline magmas in zones of continental convergence: the Tezhsar volcano-intrusive ring complex, Armenia. Lithos 320:172–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2018.08.028
Soltanmohammadi A, Grégoire M, Rabinowicz M, Gerbault M, Ceuleneer G, Rahgoshay M, Bystricky M, Benoit M (2018) Transport of volatile-rich melt from the mantle transition zone via compaction pockets: implications for mantle metasomatism and the origin of alkaline lavas in the Turkish-Iranian plateau. J of Petrol 59(12):2273–2310. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egy097
Soltanmohammadi A, Grégoire M, Ceuleneer G, Benoit M, Bédard LP, Gouy S, Rabinowicz M (2021) Origin of antecrysts in igneous rocks from the Salavat Range (NW Iran): an explanation for the geochemical signature of potassic alkaline rocks. J Petrol. 62 (7). https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egab031.6212066.
Stöcklin J (1974a) Northern Iran: Alborz Mountains, in AM, Spencer ed, Mesozoic–Cenozoic orogenic belts data for orogenic studies; Alpine-Himalayan Orogen. Geol Soc [London] Special Publication 4: 212–234.
Stöcklin J (1974b) Possible ancient continental margins in Iran. In: Drake C (ed) Burke, C. New York, Springer-Verlag, The geology of continental margins, pp 873–887
Sun SS, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol Soc, London, Special Publications 42:313–345. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Todt W, Cliff RA, Hanser A, Hofmann AW (1996) Evaluation of a 202Pb–205Pb double spike for high precision lead isotope analysis. Earth Processes: Reading the Isotopic. Code (Geophysical Monograph 95), eds Basu A, Hart SR (American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC), 6: 429–437. https://doi.org/10.1029/GM095p0429.
Ubide T, Mollo S, Zhao JX, Nazzari M, Scarlato P (2019) Sector-zoned clinopyroxene as a recorder of magma history, eruption triggers, and ascent rates. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 251:265–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2019.02.021
Verdel C, Wernicke BP, Hassanzadeh J, Guest B (2011) A Paleogene extensional arc flare up in Iran: Tectonics 30:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010TC002809
Vincent SJ, Allen MB, Ismail-Zadeh AD, Flecker R, Foland KA, Simmons MD (2005) Insights from the Talysh of Azerbaijan into the Paleogene evolution of the South Caspian region. Geol Soc Am Bull 117:1513–1533. https://doi.org/10.1130/B25690.1
Winchester JA, Floyd PA (1977) Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements. Chem Geol 20:325–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(77)90057-2
Yanagi T (2011) Arc volcano of Japan: generation of continental crust from the mantle (Vol. 136). Springer. ISBN: 9784431539957.
Zanchi A, Zanchetta S, Berra F, Mattei M, Garzanti E, Molyneux S, Nawab A, Sabouri J (2009) The Eo-Cimmerian (Late? Triassic) orogeny in North Iran. Geol Soc London Special Publications 312:31–55. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP312.3
Zartman RE, Doe BR (1981) Plumbotectonics-the model. Tectonophysics 75:135–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(81)90213-4
Zhang J, Amakawa H, Nozaki Y (1994) The comparative behaviors of yttrium and lanthanides in the seawater of the North Pacific. Geophys Res Lett 21:2677–2680. https://doi.org/10.1029/94GL02404
Zindler A, Hart S (1986) Chemical geodynamics. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sci 14:493–571. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ea.14.050186.002425
Acknowledgements
The authors thank GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research, Kiel (Germany) for providing the facilities of this research. We would like to express our sincere thanks to M. Vossoughi Abedini and M. Pourmoafi for their support throughout the studies. We would like to extent our gratitude to AR. Davoudian for his inspiring suggestions. We are also grateful to the editor-in-chief, Abdullah M. Al-Amri, and the reviewers for the comments.
Funding
The funds of this research were paid by the University of Shahid Beheshti as a research project and PhD thesis. GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research, Kiel (Germany), helped to this research by providing the facilities for electron microprobe and isotopic analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The manuscript is entitled “Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Tertiary subvolcanics from north Tehran, southern Central Alborz (Iran)”; it has not been published in any other journal. The manuscript includes original data, acquired during our own research, and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Domenico M. Doronzo
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Irannezhadi, M.R., Ghorbani, M.R., Hoernle, K.A. et al. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of tertiary subvolcanics from north Tehran, southern Central Alborz (Iran). Arab J Geosci 15, 331 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09604-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09604-3