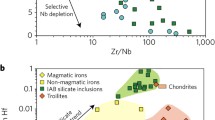
Abstract
The extreme depletion of the Earth’s mantle in sulfur is commonly seen as a signature of metal segregation from Earth’s mantle to Earth’s core. However, in addition to S, the mantle contains other elements as volatile as S that are hardly depleted relative to the lithophile volatility trend although they are potentially as siderophile as sulfur. We report experiments in metal-sulfide–silicate systems to show that the CI normalized abundances of S, Pb, and Sn in Earth’s mantle cannot be reproduced by element partitioning in Fe ± S–silicate systems, neither at low nor at high pressure. Much of the volatile inventory of the Earth’s mantle must have been added late in the accretion history, when metal melt segregation to the core had become largely inactive. The great depletion in S is attributed to the selective segregation of a late sulfide matte from an oxidized and largely crystalline mantle. Apparently, the volatile abundances of Earth’s mantle are not in redox equilibrium with Earth’s core.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albarède F (2009) Volatile accretion history of the terrestrial planets and dynamic implications. Nature 461:1227–1233
Albarède F, Ballhaus C, Blichert-Toft J, Lee C-T, Marty B, Moynier F, Yin Q-Z (2013) Asteroidal impacts and the origin of terrestrial and lunar volatiles. Icarus 222:44–52
Ballhaus C (1995) Is the upper mantle metal-saturated? Earth Planet Sci Lett 132:75–86
Ballhaus C, Laurenz V, Münker C, Fonseca ROC, Albarède F, Rohrbach A, Lagos M, Schmidt MW, Jochum K-P, Stoll B, Weis U, Helmy HM (2013) The U/Pb ratio of the Earth’s mantle—a signature of late volatile addition. Earth Planet Sci Lett 362:237–245
Borisov AA (2013) Mutual interaction of redox pairs in silicate melts: V5+/V4+/V3+/V2+ tetrad and other equilibria. Petrology 21:305–315
Boujibar A, Andrault D, Bouhifd MA, Bolfan-Casanova N, Devidal J-L, Trcera N (2014) Metal-silicate partitioning of sulphur, new experimental and thermodynamic constraints on planetary accretion. Earth Planet Sci Lett 391:42–54
Dahl TW, Stevenson DJ (2010) Turbulent mixing of metal and silicate during planet accretion—an interpretation of the Hf–W chronometer. Earth Planet Sci Lett 295:177–186
Dasgupta R, Buono A, Whelan G, Walker D (2009) High-pressure melting relations in Fe–C–S systems: Implications for formation, evolution, and structure of metallic cores in planetary bodies. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:6678–6669
Dreibus G, Palme H (1996) Cosmochemical constraints on the sulfur content in the Earth’s core. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:1125–1130
Fonseca ROC, Kirchenbaur M, Ballhaus C, Münker C, Zirner A, Gerdes A, Heuser A, Lenting C (2017) High spatial resolution isotope and trace element study of orbicular glasses from Troodos ophiolite complex: sub-arc versus shallow level fluid-mediated processes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 200:145–166
Ghiorso MS, Carmichael ISE (1987) Modelling magmatic systems: petrologic applications. Rev Mineral 17:467–499
Jacobsen SB, Harper CL (1996) Accretion and early differentiation history of the Earth based on extinct radionuclides. In: Basu A, Hart SR (eds) Earth Earth processes: reading the isotopic code. American Geophysical Union, Washington, pp 47–74
Jochum K-P, Weis U, Stoll B, Kuzmin D, Yang Q, Raczek I, Jacob DE, Stracke A, Birbaum K, Frick DA, Günther D, Enzweiler J (2011) Determination of reference values for NIST SRM 610-617 glasses following ISO guidelines. Geostand Geoanal Res 35:397–429
Jarosewich E, Nelen JA, Norberg JA (1980) Reference samples for electron microprobe analysis. Geostandard Newslett 4:43–47
Kramers JD (1998) Reconciling siderophile element data in the Earth and Moon, W isotopes and the upper lunar age limit in a simple model of homogeneous accretion. Chem Geol 145:461–478
Kilburn MR, Wood BJ (1997) Metal-silicate partitioning and the incompatibility of S and Si during core formation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 152:139–148
Kleine T, Mezger K, Palme H, Münker C (2004) The W isotope evolution of the bulk silicate Earth: constraints on the timing and mechanisms of core formation and accretion. Earth Planet Sci Lett 228:109–123
Kress VC, Ghiorso MS, Lastuka C (2004) Microsoft EXCEL spreadsheet-based program for calculating equilibrium gas speciations in the C–O–H–S–Cl–F system. Comput Geosci 30:211–214
Lagos M, Ballhaus C, Münker C, Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser C, Berndt J, Kuzmin D (2008) The Earth’s missing lead may not be in the core. Nature 456:89–92
Laurenz V, Fonseca ROC, Ballhaus C, Jochum K-P, Heuser A, Sylvester PJ (2013) The solubility of palladium and ruthenium in picritic melts: 2. the effect of sulfur. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 108:172–183
Li J, Agee CB (1996) Geochemistry of mantle-core differentiation at high pressure. Nature 381:686–689
Li J, Agee CB (2001) Element partitioning constraints on the light element composition of the Earth’s core. Geophys Res Lett 28:81–84
Li Y, Dasgupta R, Tsuno K, Monteleone B, Shimizu N (2016) Carbon and sulfur budget of the silicate Earth explained by accretion of differentiated planetary embryos. Nat Geosci. doi:10.1038/NGEO2801
Lodders K (2003) Solar system abundances and condensation temperatures of the elements. Astrophys J 591:1220–1247
Longerich HP, Jackson SE, Günther D (1996) Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric transient signal data acquisition and analyte concentration calculation. J Anal Atom Spectrom 11:899–904
Malavergne V, Tarrida M, Combes R, Bureau H, Jones J, Schwandt C (2007) New high-pressure and high-temperature metal/silicate partitioning of U and Pb: implications for the cores of the Earth and Mars. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:2637–2655
Mavrogenes JA, O’Neill HSC (1999) The relative effects of pressure, temperature and oxygen fugacity on the solubility of sulfide in mafic magmas. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:1173–1180
McDonough WF (2003) Compositional models for the Earth’s core. In: Carlson RW (ed) Treatise on geochemistry vol. 2, the mantle and core. Elsevier, Pergamon, pp 547–568
McDonough WF, Sun S-S (1995) The composition of the Earth. Chem Geol 120:223–253
Michely LT, Leitzke FP, Speelmanns IM, Fonseca ROC (2017) Competing effects of crystal chemistry and silicate melt composition on trace element behavior in magmatic systems: insights from crystal/silicate melt partitioning of the REE, HFSE, Sn, In, Ga, Ba, Pt and Rh. Contrib Mineral Petrol 172:39
Norris CA, Wood BJ (2016) Measured volatilities of important trace elements in the Earth. Plinius 42:200
O’Neill HSC (1991) The origin of the Moon and the early history of the Earth—a chemical model. The Earth. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:1155–1172
O’Neill HSC, Mavrogenes JA (2002) The sulfide capacity and the sulfur content at sulfide saturation of silicate melts at 1400 °C and 1 bar. J Petrol 43:1049–1087
Palme H, O’Neill HSC (2014) Cosmochemical estimates of mantle composition. In: Carlson RW (ed) Treatise on geochemistry vol 2. Elsevier, Pergamon, pp 1–38
Petitet JP, Petot C, Petot-Ervas G (1987) Influence of pressure on the activity of PbO in an equimolar molten PbO–SiO2 mixture. Chem Geol 62:31–34
Righter K, Drake MJ (1997) Metal-silicate equilibrium in a homogeneously accreting earth: new results for Re. Earth Planet Sci Lett 146:541–553
Righter K, Pando K, Danielson L, Lee C-T (2010) Partitioning of Mo, P and other siderophile elements (Cu, Ga, Sn, Ni Co, Cr, Mn, V and W) between metal and silicate melt as a function of temperature and silicate melt composition. Earth Planet Sci Lett 291:1–9
Rohrbach A, Ballhaus C, Golla-Schindler U, Ulmer P, Kamenetsky VS, Kuzmin DV (2007) Metal saturation in the upper mantle. Nature 449:456–458
Rohrbach A, Ballhaus C, Ulmer P, Golla-Schindler U, Schönbohm D (2011) Experimental evidence for a reduced metal-saturated upper mantle. J Petrol 52:717–731
Rubie DC, Frost DJ, Mann U, Asahara Y, Nimmo F, Tsuno K, Kegler P, Holzheid A, Palme H (2011) Heterogeneous accretion, composition and core-mantle differentiation of the Earth. Earth Planet Sci Lett 301:31–42
Rubie DC, Jacobson SA, Morbidelli A, O’Brien DP, Young ED, de Vries J, Nimmo F, Palme H, Frost DJ (2015) Accretion and differentiation of the terrestrial planets with implications for the compositions of early-formed Solar System bodies and accretion of water. Icarus 248:89–108
Schönbächler M, Carlson RW, Horan MF, Mock TD, Hauri EH (2010) Heterogeneous accretion and the moderately volatile element budget of Earth. Science 328:884–887
Sharma RC, Chang YA (1979) Thermodynamics and phase relations of transition metal-sulfur systems: part III. Thermodynamic properties of the Fe–S liquid phase and the calculation of the Fe–S phase diagram. Metall Trans 10B:103–108
van Westrenen W, Blundy J, Wood B (1999) Crystal-chemical controls on trace element partitioning between garnet and anhydrous silicate melt. Am Mineral 84:838–847
Vogel AK (2014) Siderophile element partitioning at high pressures and temperatures—implications for core formation processes. Unpubl PhD thesis, Bayreuth
Wade J, Wood BJ (2005) Core formation and the oxidation state of the Earth. Earth Planet Sci Lett 236:78–95
Wade J, Wood BJ, Tuff J (2010) Metal–silicate partitioning of Mo and W at high pressures and temperatures: evidence for late accretion of sulphur to the Earth. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 85:58–74
Wade J, Wood BJ, Tuff J (2012) Metal–silicate partitioning of Mo and W at high pressures and temperatures: evidence for late accretion of sulphur to the Earth. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 85:58–74
Wänke H (1981) Constitution of terrestrial planets. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A 303:287–302
Wänke H, Dreibus G (1988) Chemical composition and accretion history of terrestrial planets. Phil Trans R Soc Lond A 325:545–557
Wasson JT (1985) Meteorites: their record of early solar-system history. W.H. Freeman, New York
Wijbrans CH, Rohrbach A, Klemme S (2016) An experimental investigation of the stability of majoritic garnet in the Earth’s mantle and an improved majorite geobarometer. Contrib Mineral Petrol 171:50. doi:10.1007/s00410-016-1255-7
Witt-Eickschen G, O’Neill HSC (2005) The effect of temperature on the equilibrium distribution of trace elements between clinopyroxene, orthopyroxene, olivine and spinel in upper mantle peridotite. Chem Geol 221:65–101
Witt-Eickschen G, Palme H, O’Neill HSC, Allen CM (2009) The geochemistry of the volatile trace elements As, Cd, Ga, In and Sn in the Earth’s mantle: new evidence from in situ analyses of mantle xenoliths. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:1755–1778
Wood BJ, Halliday AN (2010) The lead isotopic age of the Earth can be explained by core formation alone. Nature 465:767–771
Wood BJ, Kiseeva ES, Mirolo FJ (2014) Accretion and core formation: the effects of sulfur on metal-silicate partition coefficients. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2014.09.002
Acknowledgements
We thank Dieter Lülsdorf of the mechanical workshop for technical assistance, Thomas Schulz for helping with all aspects of experimentation, and Nils Jung for lapidary work. Comments by Balz Kamber, Herbert Palme, Jon Wade, and Sasha Borisov greatly helped in clarifying the arguments presented here. C.B., A.R, and A.K.V acknowledge financial support by the DFG through Grants Ba 964/26, SFB 170 (“Late Accretion of Terrestrial Planets”), and Ru 1323/2 within the SPP 1385 (“The First 10 Million Years of the Solar System”), respectively. We thank Jochen Hoefs for careful editorial handling of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jochen Hoefs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ballhaus, C., Fonseca, R.O.C., Münker, C. et al. The great sulfur depletion of Earth’s mantle is not a signature of mantle–core equilibration. Contrib Mineral Petrol 172, 68 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-017-1388-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-017-1388-3