Abstract.
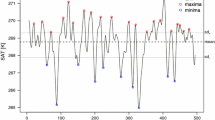
Statistical analyses of monthly mean sea surface temperatures (SST) from observations and from a hierarchy of global coupled ocean–atmosphere models were carried out with the focus on the midlatitudes (25°N–50°N). The spectra of the simulated SSTs have been tested against the null hypothesis of Hasselmann's stochastic climate model, which assumes an AR(1)-process for the SST variability in its simplest version. It was found that the spectra of the SST variability in the observations and in the CGCMs with fully dynamical ocean models differ significantly from AR(1)-processes, while the SST variability in an AGCM coupled to a slab ocean is consistent with an AR(1)-process. The deviations of the SST spectra from the fitted AR(1) spectra are not due to spectral peaks but are due to a slower increase of variance from seasonal to decadal time scales. Parts of these differences can be attributed to the interaction between the mixed layer and the sub-mixed-layer ocean. While the mixed layer depth variability generates SST variability on seasonal and shorter time scales, the heat exchange with the deep ocean, reduces variability on longer time scales.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dommenget, .D., Latif, .M. Analysis of observed and simulated SST spectra in the midlatitudes. Climate Dynamics 19, 277–288 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-002-0229-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-002-0229-9