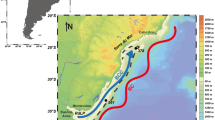
Abstract
Although global thermohaline circulation pathways are fairly well known, the same cannot be said for local circulation pathways. Within the southwest Indian Ocean specifically there is little consensus regarding the finer point of thermohaline circulation. We present recently collected multibeam bathymetry and PARASOUND data from the northern Natal Valley and Mozambique Ridge, southwest Indian Ocean. These data show the Ariel Graben, a prominent feature in this region, creates a deep saddle across the Mozambique Ridge at ca. 28°S connecting the northern Natal Valley with the Mozambique Basin. Results show a west to east change in bathymetric and echo character across the northern flank of the Ariel Graben. Whereby eroded plastered sediment drifts in the west give way to aggrading plastered sediment drift in the midgraben, terminating in a field of seafloor undulations in the east. In contrast, the southern flank of the Ariel Graben exhibits an overall rugged character with sediments ponding in bathymetric depressions in between rugged sub/outcrop. It is postulated that this change in sea-floor character is the manifestation of deep water flow through the Ariel Graben. Current flow stripping, due to increased curvature of the graben axis, results in preferential deposition of suspended load in an area of limited accommodation space consequently developing an over-steepened plastered drift. These deposited sediments overcome the necessary shear stresses, resulting in soft sediment deformation in the form of down-slope growth faulting (creep) and generation of undulating sea-floor morphology. Contrary to previous views, our works suggests that water flows from west to east across the Mozambique Ridge via the Ariel Graben.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alley RB, Clark PU, Keigwin LD, Webb RS (1999) Making sense of millennial-scale climate change. In: Clark PU, Webb RS, Keigwin LD (eds) Mechanisms of Global Climate Change at Millennial Time Scales. AGU Geophys Monogr 112:385–494
Bang ND, Pearce AF (1976) Large-scale circulation of surface water of the south Indian Ocean. In: Heydorn AEF (ed) Ecology of the Agulhas current region–an assessment of biological responses to environmental parameters in the south–west Indian Ocean. Proceedings of the marine freshwater conference, port Elizabeth. CSIR, Pretoria, pp 4–10
Beal LM, Bryden HL (1997) Observations of an Agulhas undercurrent. Deep-Sea Res I 44:1715–1724. doi:10.1016/S0967-0637(97)00033-2
Beal LM, Bryden HL (1999) The velocity and vorticity structure of the Agulhas current at 32° S. J Geophys Res 104(C3):5151–5176
Ben-Avraham Z, Niemi TM, Hartnady CJH (1994) Mid-tertiary changes in deep ocean circulation patterns in the natal valley and Transkei basin, southwest Indian ocean. Earth Planet Sci Lett 121(3–4):639–646
Blome MW, Cohen AS, Tyron CA, Brooks JR (2012) The environmental context for the origins of modern human diversity: a synthesis of regional variability in African climate 150,000--30,000 years ago. J Hum Evol 62:563--592
Carter L, Carter RM, Nelson CS, Fulthorpe CS, Neil HL (1990) Evolution of Pliocene to recent abyssal sediment waves on Bounty Channel levees, New Zealand. Mar Geol 95:97–109
Casal TGD, Beal LM, Lumpkin R (2006) A North Atlantic deep-watereddy in the Agulhas Current system. Deep-Sea Res I 53:1718–1728
Cawthra HC, Neumann FH, Uken R, Smith AM, Guastella L, Yates AM (2012) Sedimentation on the narrow (8 km wide), oceanic current-influenced continental shelf off Durban, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Mar Geol 323–325:107–122
Cunningham AP, Barker PF (1996) Evidence for westward-flowing Weddell Sea Deep Water in the Falkland Trough, western South Atlantic. Deep-Sea Res 43:643–654
Damuth JE (1975) Echo characters of the western equatorial Atlantic floor and its relationship to the dispersal and distribution of terrigenous sediments. Mar Geol 18:17–45
Damuth JE (1980) Use of high-frequency (3.5–12 kHz) echograms in the study of near- bottom sedimentation processes in the deep sea: a review. Mar Geol 38:51–75
Damuth JE, Hayes DE (1977) Echo character of the east Brazilian continental margin and its relationship to sedimentary processes. Mar Geol 24:73–95
de Ruijter WPM, Biastoch A, Drijfhout SS, Lutjeharms JRE, Matano RP, Pichevin T, van Leeuwen PJ, Weijer W (1999) Indian-Atlantic interocean exchange: dynamics, estimation and impact. J Geophys Res 104:20885–20910
de Ruijter WPM, Ridderinkhof H, Lutjeharms JRE, Schouten MW, Veth C (2002) Observations of the flow in the Mozambique channel. Geophys Res Lett 29(10):1401–1403
de Ruijter WPM, van Aken HM, Beier EJ, Lutjeharms JRE, Matano RP, Schouten MW (2003) Eddies and dipoles around south Madagascar: formation, pathways and large-scale impact. Deep-Sea Res I 51:383–400
Dengler L, Carver GA, McPherson R (1993) Sources of north coast seismicity. Calif Geol 45:40–53
Dillon WP, Lee MW, Fehlhaber K, Coleman DF (1993) Gashydrates on the Atlantic margin of the United States—controls on concentration. In Howell DG (ed) the future of energy gases. Geol Surv Prof Pap 1570:313–330
DiMarco SF, Chapman P, Nowlin WD Jr, Hacker P, Donohue K, Luther M, Johnson GC, Toole J (2002) Volume transport and property distributions of the Mozambique channel. Deep-Sea Res II: Top Stud Oceanogr 49(7–8):1481–1511
Dingle RV, Robson S (1985) Slumps, canyons and related features on the continental margin off East London, SE Africa (SW Indian Ocean). Mar Geol 67:37–54
Dingle RV, Goodlad SW, Martin AK (1978) Bathymetry and stratigraphy of the northern Natal Valley (SW Indian Ocean): a preliminary account. Mar Geol 28:89–106
Dingle RV, Birch GF, Bremner JM, De Decker RH, du Plessis A, Engelbrecht JC, Fincham MJ, Fitton T, Flemming BW, Goodlad SW, Gentle RI, Martin AK, Mills EG, Moir GJ, Parker RJ, Robson SH, Rogers J, Salmon DA, Siesser WG, Simpson ESW, Summerhayes CP, Westall F, Winter A, Woodborne MW (1987) Deep-sea sedimentary environments around southern Africa (SE-Atlantic & SW-Indian Oceans). Ann S Afr Mus 98:1–27
Donohue KA, Toole JM (2003) A near-synoptic survey of the Southwest Indian Ocean. Deep-Sea Res II 50:1893–1931
Donohue KA, Firing E, Beal L (2000) Comparison of three velocity sections of the Agulhas current and Agulhas undercurrent. J Geophys Res Oceans 105(C12):28585–28593
Dorn WU, Werner F (1993) The contour-current flow along the southern Iceland-Faeroe Ridge as documented by its bedforms and asymmetrical channel fillings. Sediment Geol 82:47–59
Faugères JC, Stow DAV, Imbert P, Viana A (1999) Seismic features diagnostic of contourite drifts. Mar Geol 162:1–38
Faugères JC, Gonthier E, Mulder T, Kenyon N, Cirac P, Griboulard R, Berné S, Lesuavé R (2002) Multi-process generated sediment waves on the Landes plateau (Bay of Biscay, North Atlantic). Mar Geol 182(3–4):279–302
Flemming BW (1980) Sand transport and bedform patterns on the continental shelf between Durban and Port Elizabeth (Southeast African Continental Margin). Sediment Geol 26:179–205
Flemming B, Hay R (1988) Sediment distribution and dynamics of the Natal continental shelf, in Coastal Ocean Studies off Natal, South Africa, Lecture Notes. In: Schumann EH (ed) Coastal estuarine stud, vol 26. Springer, Berlin, pp 47–80
Flood RD (1980) Deep-sea sedimentary morphology: modelling and interpretation of echo-sounding profiles. Mar Geol 38:77–92
Flood RD (1994) Abyssal bedforms as indicators of changing bottom current flow: Examples from the U.S. East Coast continental rise. Paleoceanography 9:1049–1060
Flood RD, Shor AN, Manley PD (1993) Morphology of abyssal mudwaves at Project MUDWAVES sites in the Argentine Basin. Deep-Sea Res 40:859–888
Galbraith ED, Jaccard SL, Pedersen TF, Sigman DM, Haug DH, Cook M, Southon JR, Francois R (2007) Carbon dioxide release from the North Pacific abyss during the last deglaciation. Nature 449:890–893
Gardner J, Prior D, Field M (1999) Humboldt Slide—a large shear dominated retrogressive slope failure. Mar Geol 154:323–338
Goodlad SW (1986) Tectonic and sedimentary history of the mid-Natal Valley (SW Indian Ocean). Joint Geological Survey/University of Cape Town. Mar Geosci Unit Bull 15:415
Green AN (2009) Sediment dynamics on the narrow, canyon-incised and current-swept shelf of the northern KwaZulu-Natal continental shelf, South Africa. Geo-Mar Lett 29:201–219
Green AN (2011a) Submarine canyons associated with alternating sediment starvation and shelf-edge wedge development: Northern KwaZulu-Natal continental margin, South Africa. Mar Geol 289:114–126
Green AN (2011b) The late Cretaceous to Holocene sequence stratigraphy of a sheared passive upper continental margin, northern KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Mar Geol 289:17–28
Green AN, Uken R (2008) Submarine landsliding and canyon evolution on the northern KwaZulu-Natal continental shelf, South Africa, SW Indian Ocean. Mar Geol 254:152–170
Green AN, Goff JA, Uken R (2007) Geomorphological evidence for upslope canyon-forming processes on the northern KwaZulu-Natal shelf, South Africa. Geo-Mar Lett 27:399–409
Gutjahr M, Hoogakker BAA, Frank M, McCave IN (2010) Changes in North Atlantic Deep Water strength and bottom water masses during Marine Isotope Stage 3 (45–35 ka BP). Quat Sci Rev 29:2451–2461. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.02.024
Henry LA, Frank N, Hebbeln D, Wienberg C, Robinson L, de Flierdt T, Dahl M, Douarin M, Morrison CL, Correa ML, Rogers AD, Ruckelshausen M, Roberts JM (2014) Global ocean conveyor lowers extinction risk in the deep sea. Deep-Sea Res Part I: Oceanogr Res Pap 88:8–16
Hill PR, Moran KM, Blasco SM (1982) Creep deformation of slope sediments in the Canadian Beaufort Sea. Geo-Mar Lett 2:163–170
Holbrook W (2001) Seismic studies of the Blake Ridge: implications for hydrate distribution, methane expulsion, and free gas dynamics. In: Paull C, Dillon W (eds) Natural Gas Hydrates: Occurrence, Distribution, and Detection. American Geophysical Union, Geophysical Monograph 124:235–256
Holbrook W, Lizarralde D, Pecher I, Gorman A, Hackwith K, Hornbach M, Saffer D (2002) Escape of methane gas through sediment waves in a large methane hydrate province. Geology 30(5):467–470
Howe JA (1996) Turbidite and contourite sediment waves in the northern Rockall Trough, North Atlantic Ocean. Sedimentology 43:219–234
Jacobi RD (1982) Microphysiographie du Sud-Est de l’Atlantique Nord et ses conséquences pour la distribution des processus prés du fond marin et des faciès associés, vol 31. Bull Inst Geol Bassin Aquitaine, Bordeaux, pp 31–46
Jokat W (2006) Southeastern Atlantic and Southwestern Indian Ocean: reconstruction of the sedimentary and tectonic development since the cretaceous, AISTEK-II: Mozambique Ridge and Mozambique Basin. Report of the RV “Sonne” Cruise SO-183, Project AISTEK-II 20 May to 7 July 2005 reports on Polar and Marine Research. Alfred-Wegener-Institute for Polar and Marine Research, Bremerhaven, p 71
Jokat W (2009) The expedition of the research vessel “Pelagia” to the Natal Basin and the Mozambique Ridge in 2009 (Project AISTEK III). Alfred-Wegener- Institute for Polar and Marine Research, Bremerhaven, p 67
Kenyon NH (1986) Evidence from bedforms for a strong poleward current along the upper continental slope of NW Europe. Mar Geol 72:187–198
Kenyon NH, Belderson RH (1973) Bedforms of the Mediterranean undercurrent observed with sidescan sonar. Sediment Geol 9:77–99
Kenyon NH, Belderson RH, Stride AH (1978) Channels, canyons and slump folds on the continental slope between south-west Ireland and Spain. Oceanol Acta 1:369–380
Kidd RB, Lucchi RG, Gee M, Woodside JM (1998) Sedimentary processes in the Stromboli Canyon and Marsili Basin, SE Tyrrhenian Sea: results from sidescan sonar surveys. Geo-Mar Lett 18:146–154
Lee SH, Chough SK (2001) High-resolution (2–7 kHz) acoustic and geometric characters of submarine creep deposits in the South Korea Plateau, East Sea. Sedimentology 48:629–644
Lee HJ, Syvitski JPM, Parker G, Orange D, Locat J, Hutton EWH, Imran J (2002) Distinguishing sediment waves from slope failure deposits: field examples, including the “Humboldt Slide”, and modelling results. Mar Geol 192:79–104
Leinweber VT, Jokat W (2011) Is there continental crust underneath the Northern Natal Valley and the Mozambique Coastal Plains? Geophys Res Lett 38:L14303
Leinweber VT, Jokat W (2012) The Jurassic history of the Africa-Antarctica Corridor - new constraints from magnetic data on the conjugate continental margins. Tectonophysics 530–531:87–101. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2011.11.008
Li C, von Storch JS, Marotzke J (2013) Deep-ocean heat uptake and equilibrium climate response. Climate Dynam 40(5–6):1071–1086
Lonsdale P, Malfait B (1974) Abyssal dunes of foraminiferal sand on the Carnegie Ridge. GSA Bull 85:1697–1712
Lonsdale PF, Speiss FN (1977) Abyssal bedforms explored with a deeply towed instrument package. Mar Geol 23:57–75
Lutjeharms JRE (2006a) The Agulhas current. Springer, Berlin, p 329
Lutjeharms JRE (2006b) The coastal oceans of south-eastern Africa. In: Robinson AR, Brink KH (eds) The Sea, vol 14B. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, pp 783–834
Lutjeharms JRE (2007) Three decades of research on the greater Agulhas current. Ocean Sci 3(1):129–147
Maldonado A, Barnolas A, Bohoyo F, Galindo-Zaldívar J, Hernández-Molina J, Lobo F, Rodríguez-Fernández J, Somoza L, Tomás Vázquez J (2003) Contourite deposits in the central Scotia Sea: the importance of the Antarctic circumpolar current and the Weddell gyre flows. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 198(1–2):187–221
Malinverno A, Ryan WBF, Auffret G, Pautot G (1998) Sonar images of the path of recent failure events on the continental margin off Nice, France. GSA Spec Pap 229:59–76
Manley PL, Caress DW (1994) Mudwaves on the Gardar sediment drift, NE Atlantic. Paleoceanography 9:973–988
Martin AK (1981a) The influence of the Agulhas current on the physiographic development of the northernmost Natal Valley (SW Indian ocean). Mar Geol 39:259–276
Martin AK (1981b) Evolution of the Agulhas current and its palaeoecological implications. S Afr J Sci 77:547–554
Martin AK (1987) A comparison of sedimentation rates in the Natal Valley, S.W. Indian Ocean, with modern sediment yields in east coast Rivers, Southern Africa. S Afr J Sci 83:716–724
Martin AK, Hartnady CJH (1986) Plate tectonic development of the south West Indian Ocean: A revised reconstruction of East Antarctica and Africa. J Geophys Res 91:4767–4786
Martínez-Méndez G, Zahn R, Hall IR, Pena LD, Cacho I (2008) 345,000-year-long multi-proxy records off South Africa document variable contributions of northern versus southern component water to the deep south Atlantic. Earth Planet Sci Lett 267(1–2):309–321
Masson DG, Watts AB, Gee MJR, Urgeles R, Mitchell NC, Le Bas TP, Canals M (2002) Slope failures on the flanks of the western Canary Islands. Earth Sci Rev 57(1–2):1–35. doi:10.1016/S0012-8252(01)00069-1
McDonagh EL, Bryden HL, King BA, Sanders RJ (2008) The circulation of the Indian Ocean at 32°S. Prog Oceanogr 79:20–36
Menary M, Scaife A (2014) Naturally forced multidecadal variability of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation. Climate Dynam 42(5–6):1347–1362
Migeon S, Savoye B, Faugeres J-C (2000) Quaternary development of migrating sediment waves in the Var deep-sea fan: distribution, growth pattern, and implication for levee evolution. Sediment Geol 133:265–293
Migeon S, Savoye B, Zanella E, Mulder T, Faugeres J-C, Weber O (2001) Detailed seismic-reflection and sedimentary study of turbidite sediment waves on the Var Sedimentary Ridge (SE France): significance for sediment transport and deposition and for the mechanics of sediment-wave construction. Mar Pet Geol 18:179–208
Morris SA, Kenyon NH, Limonov AF, Alexander J (1998) Downstream changes of large-scale bedforms in turbidites around the Valencia channel mouth, north-west Mediterranean: implications for paleoflow reconstruction. Sedimentology 45:365–377
Nakajima T, Satoh M (2001) The formation of large mudwaves by turbidity currents on the levees of the Toyama deep-sea channel, Japan Sea. Sedimentology 48:435–463
Niemi TM, Ben-Avraham Z, Hartnady CJH, Reznikov M (2000) Post-Eocene seismic stratigraphy of the deep ocean basin adjacent to the southeast African continental margin: a record of geostrophic bottom current systems. Mar Geol 162(2–4):237–258
Normark WR, Hess GR, Stow DAV, Bowen AJ (1980) Sediment waves on the Monterey Fan levee: a preliminary physical interpretation. Mar Geol 37:1–18
O’Leary DWO, Laine E (1996) Proposed criteria for recognizing intrastratal deformation features in marine high resolution seismic reflection profiles. Geo-Mar Lett 16:305–312
Pearce AF (1977) Some features of the upper 500m of the Agulhas current. J Mar Res 35(4):731–753
Piper DJW, Shor AN, Farre JA, O’Connell S, Jacobi R (1985) Sediment slides and turbidity currents on the Laurentian Fan: sidescan sonar observations near the epicentre of the 1929 Grand Banks earthquake. Geology 13:538–541
Polzin KL, Toole JM, Ledwell JR, Schmitt RW (1997) Spatial variability of turbulent mixing in the abyssal ocean. Science 276:93–96
Preu B, Spieß V, Schwenk T, Schneider RR (2011) Evidence for current-controlled sedimentation along the southern Mozambique continental margin since Early Miocene times. Geo-Mar Lett 31(5–6):427–435. doi:10.1007/s00367-011-0238-y
Quartly GD, Srokosz MA (2004) Eddies in the southern Mozambique channel. Deep-Sea Res Part II: Top Stud Oceanogr 51(1–3):69–83
Raymo ME, Ruddiman WF, Shackleton NJ, Oppo DW (1990) Evolution of Atlantic-pacific gradients over the last 2.5 m.y. Earth Planet Sci Lett 97:353–368
Raymo ME, Oppo DW, Curry W (1997) The mid-Pleistocene climate transition: a deep sea carbon isotopic perspective. Paleoceanography 12:546–559
Rutberg RL, Hemming SR, Goldstein SL (2000) Reduced north Atlantic deep water flux to the glacial southern ocean inferred from neodymium isotope ratios. Nature 405:935–938
Saria E, Calais E, Stamps DS, Delvaux D, Hartnady CJH (2014) Present-day kinematics of the East African rift. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 119:3584–3600. doi:10.1002/2013JB010901
Schlüter P, Uenzelmann-Neben G (2008) Indications for bottom current activity since Eocene times: the climate and ocean gateway archive of the Transkei basin, South Africa. Global Planet Change 60:416–428
Schmieder F, von Dobeneck T, Bleil U (2000) The Mid-Pleistocene climate transition as documented in the deep South Atlantic ocean: initiation, interim state and terminal event. Earth Planet Sci Lett 179:539–549
Schwehr K, Driscoll N, Tauxe L (2007) Origin of continental margin morphology: Submarine-slide or downslope current-controlled bedforms, a rock magnetic approach. Mar Geol 240:19–41. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2007.01.012
Shillington DJ, Seeber L, Sorlien CC, Steckler MS, Kurt H, Dondurur D, Çifçi G, İmren C, Cormier MH, McHugh CMG, Gürçay S, Poyraz D, Okay S, Atgın O, Diebold JB (2012) Evidence for widespread creep on the flanks of the Sea of Marmara transform basin from marine geophysical data. Geology 40(5):439–442
Srinivasan A, Garraffo Z, Iskandarani M (2009) Abyssal circulation in the Indian ocean from a resolution global hindcast. Deep-Sea Res I: Oceanogr Res Pap 56(11):1907–1926
Stow DAV, Mayall M (2000) Deep-water sedimentary systems: New models for the 21st century. Mar Pet Geol 17(2):125–135
Stow DAV, Reading HG, Collison JD (1996) Deep seas. In: Reading HG (ed) Sedimentary environments: processes, facies and stratigraphy. Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp 395–453
Stramma L, Lutjeharms JRE (1997) The flow field of the subtropical gyre of the south Indian ocean. J Geophys Res 102:5513–5530
Syvitski JPM, Burrell DC, Skei JM (1987) Fjords: Processes and Products. Springer Verlag, New York, p 379
Tinti S, Maramai A, Favali P (1995) The gargano promontory: an important Italian seismogenetic–tsunamigenic area. Mar Geol 122:227–241
Toole JM, Warren BA (1993) A hydrographic section across the subtropical South Indian Ocean. Deep-Sea Res I 40:1973–2019
Trincardi F, Cattaneo A, Correggiari A, Ridente D (2004) Evidence of soft sediment deformation, fluid escape, sediment failure and regional weak layers within the late quaternary mud deposits of the Adriatic Sea. Mar Geol 213(1–4):91–119
Tucholke BE (1979) Furrows and focuses echoes on the Blake outer ridge. Mar Geol 31:13–20
Ullgren JE, van Aken HM, Ridderinkhof H, de Ruijter WPM (2012) The hydrography of the Mozambique channel from six years of continuous temperature, salinity, and velocity observations. Deep-Sea Res I Oceanogr Res Pap 69:36–50
van Aken HM, Ridderinkhof H, de Ruijter WPM (2004) North Atlantic deep water in the south-western Indian ocean. Deep-Sea Res I 51:755–776
Wiles E, Green A, Watkeys M, Jokat W, Krocker R (2013) The evolution of the Tugela canyon and submarine fan: a complex interaction between margin erosion and bottom current sweeping, southwest Indian Ocean, South Africa. Mar Pet Geol 44:60–70
Wiles E, Green A, Watkeys M, Jokat W, Krocker R (2014) Anomalous seafloor mounds in the northern natal valley, southwest Indian Ocean: implications for the east African rift system. Tectonophysics 630:300–312. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2014.05.030
Winter A, Martin, AK (1990) Late Quaternary history of the Agulhas Current. Paleoceanography 5(4):479–486
Wynn RB, Stow DAV (2002) Classification and characterisation of deep-water sediment waves. Mar Geol 192:7–22
Wynn RB, Masson DG, Stow DAV, Weaver PPE (2000a) Turbidity current sediment waves on the submarine slopes of the western Canary Islands. Mar Geol 163:185–198
Wynn RB, Weaver PPE, Ercilla G, Stow DAV, Masson DG (2000b) Sedimentary processes in the Selvage sediment-wave field, NE Atlantic: new insights into the formation of sediment waves by turbidity currents. Sedimentology 47:1181–1197
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the BMBF (Bundesministerium fur Bildung und Forschung) for funding the scientific projects (contract numbers 03G0183A, 03G0730A). The crews of RV Sonne (AISTEK II) and RV Pelagia (AISTEK III) are acknowledged for their excellent support and expertise in the data acquisition phases. The financial assistance of the National Research Foundation (Innovation Scholarship) (83799) towards this research is hereby acknowledged. Opinions expressed and conclusions arrived at, are those of the authors and are not necessarily to be attributed to the DAAD-NRF. Prof. Dr. BW Flemming and Dr. AK Martin are thanked for their welcomed reviews of the initial manuscript. Their input added greatly to the revised manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiles, E., Green, A., Watkeys, M. et al. A new pathway for Deep water exchange between the Natal Valley and Mozambique Basin?. Geo-Mar Lett 34, 525–540 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-014-0383-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-014-0383-1