Abstract
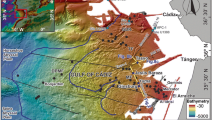
The Sorokin Trough (Black Sea) is characterized by diapiric structures formed in a compressional tectonic regime that facilitate fluid migration to the seafloor. We present acoustic data in order to image details of mud volcanoes associated with the diapirs. Three types of mud volcanoes were distinguished: cone-shaped, flat-topped, and collapsed structures. All mud volcanoes, except for the Kazakov mud volcano, are located above shallow mud diapirs and diapiric ridges. Beyond the known near-surface occurrence of gas hydrates, bottom simulating reflectors are not seen on our seismic records, but pronounced lateral amplitude variations and bright spots may indicate the presence of gas hydrates and free gas.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhmetjanov A, Akhmanov G, Krylov O, Basov R, Kozlova E, Stadnitskaya A (1996) Mud volcanoes of the Kerch Peninsula: general review. MarinF (UNESCO) 100:23–24
Bohrmann G, Schenck S (2002) RV Meteor Cruise Report M52/1, MARGASCH, Marine gas hydrates in the Black Sea. GEOMAR Research Center, Kiel
Bohrmann G, Ivanov M, Foucher J-P, Spiess V, Bialas J, Greinert J, Weinrebe W, Abegg F, Aloisi G, Artemov Y, Blinova V, Drews M, Heidersdorf F, Krabbenhöft A, Klaucke I, Krastel S, Leder T, Polikarpov I, Saburova M, Schmale O, Seifert R, Volkonskaya A, Zillmer M (2003) Mud volcanoes and gas hydrates in the Black Sea—new data from Dvurechenskii and Odessa mud volcanoes. Geo-Mar Lett 23(3/4) (in press) DOI 10.1007/s00367-003-0157-7
Bouriak SV, Akhemtjanov AM (1998) Origin of gas hydrate accumulations on the continental slope of the Crimea from geophysical studies. In: Henriet JP, Mienert J (eds) Gas hydrates; relevance to world margin stability and climate change. Geol Soc Spec Publ, pp 215–222
Bouriak S, Vanneste M, Saoutkine A (2000) Inferred gas hydrates and clay diapirs near the Storegga Slide on the southern edge of the Vøring Plateau, offshore Norway. Mar Geol 163:125–148
Brown KM (1990) Nature and hydrogeologic significance of mud diapirs and diatremes for accretionary systems. J Geophys Res 95:8969–8982
Dillon WP, Paull CK (1983) Marine gas-hydrates. II. Geophysical evidence. In: Cox JL (ed) Natural gas hydrates, properties, occurrence and recovery. Butterworth, Woburn, MA, pp 73–90
Finetti IR (1988) Monograph on the Black Sea. Morelli Editore, Trieste
Gaynanov VG, Bouriak SV, Ivanov MK (1998) Seismic evidence for gas accumulation related to the area of mud volcanism in the deep Back Sea. Geo-Mar Lett 18:139–145
Ginsburg GD, Kremlev AN, Grigor MN, Larkin GV, Pavlenkin AD, Saltykova NA (1990) Filtrogenic gas hydrates in the Black Sea (21st voyage of the research vessel Evpatoriya). Soviet Geol Geophys 31:8–16
Higgins GE, Saunders JB (1974) Mud volcanoes—their nature and origin. Verh Naturforsch Ges Basel 84:101–152
Ivanov MK, Limonov AF, van Weering TCE (1996) Comparative characteristics of the Black Sea and Mediterranean Ridge mud volcanoes. Mar Geol 132:253–271
Ivanov MK, Limonov AM, Woodside JM (1998) Extensive deep fluid flux through the sea floor on the Crimean continental margin (Black Sea). In: Henriet JP, Mienert J (eds) Gas hydrates; relevance to world margin stability and climate change. Geol Soc Spec Publ, pp 195–214
Kopf AJ (2002) Significance of mud volcanism. Rev Geophys 40:1–52
Kopf A, Behrmann JH (2000) Extrusion dynamics of mud volcanoes on the Mediterranean Ridge accretionary complex. In: Vendeville B, Mart Y, Vigneresse J-L (eds) From the Arctic to the Mediterranean: salt, shale, and igneous diapirs in and around Europe. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 174:169–204
Kopf A, Robertson AHF, Clennell MB, Flecker R (1998) Mechanism of mud extrusion on the Mediterranean Ridge. Geo-Mar Lett 18:97–114
Kutas RI, Rusakov OM, Kobolev VP (2002) Gas seeps in northwestern Black Sea: geological and geophysical studies. Russian Geol Geophys 47:664–670
Limonov AF, Woodside JM, Ivanov MK (1994) Mud volcanism in the Mediterranean and Black Seas and shallow structure of the Eratosthenes Seamount. UNESCO Rep Mar Sci 64
Limonov AF, van Weering TCE, Kenyon NH, Ivanov MK, Meisner LB (1997) Seabed morphology and gas venting in the Black Sea mud volcano area: observations with the MAK-1 deep-tow sidescan sonar and bottom profiler. Mar Geol 137:121–136
Milkov AV (2000) Worldwide distribution of submarine mud volcanoes and associated gas hydrates. Mar Geol 167:29–42
Okay AI, Sengör AMC, Görür N (1994) Kinematic history of the opening of the Black Sea and its effect on the surrounding regions. Geology 22:267–270
Paull CK, Matsumoto R, Wallace P et al. (1996) Proc Ocean Drilling Program, Initial Reports 164. Ocean Drilling Program, College Station, TX
Rakhmanov RR (1987) Mud volcanoes and their value in predicting oil and gas resources (in Russian). Nedra, Moscow
Reed DL, Silver EA, Tagudin JE, Shipley TH, Vrolijk P (1990) Relations between mud volcanoes, thrust deformation, slope sedimentation, and gas hydrates, offshore north Panama. Mar Petrol Geol 7:44–54
Ross DA, Uchupi E, Prada KE, MacIlvaine JC (1974) Bathymetry and microtopography of Black Sea. In: Ross DA, Egens ET (eds) The Black Sea—geology, chemistry and biology. Am Assoc Petrol Geol Mem, pp 1–10
Soloviev V, Ginsburg GD (1994) Formation of submarine gas hydrates. Bull Geol Soc Denmark 41:86–94
Stamatakis MG, Baltatzis EG, Skounakis SB (1987) Sulfate minerals from a mud volcano in the Katakolo area, western Pelepones, Greece. Am Mineral 72:839–841
Tugolesov DA, Gorshkov AS, Meisner LB, Solov’ev VV, Khakhalev EM (1985) Tectonics of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic deposits of the Black Sea Basin (in Russian). Nedra, Moscow
Woodside JM, Ivanov MK, Limonov AF (1997) Neotectonics and fluid flow through seafloor sediments in the Eastern Mediterranean and Black Seas. Parts I and II. UNESCO IOC Tech Ser no 48
Yefremova AG, Zhizhchenko BP (1974) Occurrence of crystalline hydrates from gases in precipitates of present-day oceanic regions (in Russian). Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 214:1179–1181
Acknowledgments
We thank the scientists and crew of cruise TTR-6 and Meteor cruise M52/1 for their help in collecting the data. Comments by S. De Beukelaer, R. Kutas, and C. Moore significantly improved this paper. Our research was funded by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Kr 2222/4-1) and the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung. This is publication GEOTECH-30 of the program GEOTECHNOLOGIEN of the BMBF and DFG (grant 03G0566A; collaborative project OMEGA) and publication RCOM0089 of the DFG-Research Center “Ocean Margins” (University of Bremen).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krastel, S., Spiess, V., Ivanov, M. et al. Acoustic investigations of mud volcanoes in the Sorokin Trough, Black Sea. Geo-Mar Lett 23, 230–238 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-003-0143-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-003-0143-0