Abstract
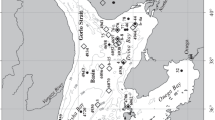
Data presented and discussed here were collected continuously during April/May 1975 in the Bornholm Basin of the Baltic Sea. Sedimentation rates of particulate matter were recorded with 5 multisample sediment traps from different depths in the water column at 2 positions 170 km apart. Current meter data collected during the same period and depths indicated that the positions remained hydrographically distinct during the investigation. Particulate matter from the euphotic zone including diatom cells formed the bulk of the material collected by all traps. This flux of organic particles to the bottom was unimpeded by the strong density stratification present in the water column. The upper traps always collected less material than lower ones. This paradox has been ascribed to diminishing current speeds with depth, concomitant with an increase in sinking rates of phytoplankton and phytodetritus. Both factors influence the sampling efficiency of sediment traps, which are thought to have underestimated actual sedimentation rates here. A time lag of 2 to 3 weeks in bloom development seemed responsible for the characteristic differences between the two positions. The phase of major sedimentation at one position covered about 18 days, and a distinct sequence in the composition of the material collected by the 6 glasses of each trap indicated phases of a progressively deteriorating phytoplankton population in the water column contributing the particulate material. A total of 6.2 g C m-2 in 34 days was recorded at this station. Apart from a trap situated in an oxygen deficient layer which collected 0.44 g C m-2 of zooplankton corpses, zooplankton mortality was overestimated by the traps. Large-scale sedimencation of “fresh” organic matter produced by the spring bloom is probably a regular feature in areas with low over-wintering zooplankton populations and, as such, possibly has a direct stimulatory effect on growth and reproduction of the benthos.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Bröckel, K. von: Der Energiefluß im pelagischen Ökosystem vor Boknis Eck (Westliche Ostsee), 96 pp. Dissertation, Universität Kiel 1975
Derenbach, J.: Zur Homogenisation des Phytoplanktons für die Chlorophyllbestimmung. Kieler Meeresforsch. 25, 166–171 (1969)
Dietrich, G. und F. Schott: Wasserhaushalt und Strömung. In: Meereskunde der Ostsee, pp 33–42. Hrsg. von L. Magaard und G. Rheinheimer. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag 1974
Gardner, W.D.: Fluxes, dynamics, and chemistry of particulates in the ocean, 402 pp. Ph.D. Thesis, M.I.T./Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Joint Program in Oceanography 1977. (Copies available from: W.D. Gardner, Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory of Columbia University, Palisades, New York 10964, USA)
Hendrikson, P.: Auf- und Abbauprozesse partikulärer organischer Substanz anhand von Sestonund Sinkstoffanalysen, 160 pp. Dissertation, Universität Kiel 1975
Keunecke, K.H., H. Kohn, W. Krauß, G. Miosga, F. Schott, P. Speth, J. Willebrand und W. Zenk: BALTIC '75 — physikalischer Teil —, Messungen des IfM, der FWG und der DFVLR. Ber. Inst. MeeresKde Kiel 11, 1–100 (1975)
Kielmann, J., J. Holtorf and U. Reimer: Data Report BALTIC '75. Ber. Inst. MeeresKde Kiel 26, 1–155 (1976)
Kögler, F.C. and B. Larsen: The West Bornholm basin in the Baltic Sea. Geological structure and quaternary sediments. Boreal (In press)
Krause, G.: Ein Beitrag zum Problem der Erneuerung des Tiefenwassers im Arkona Becken. Kieler Meeresforsch. 25, 268–271 (1969)
Lenz, J.: Zur Methode der Sestonbestimmung. Kieler Meeresforsch. 27, 180–193 (1971)
Lorenzen, C.J.: Determination of chlorophyll and pheopigments: spectrophotometric equations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 12, 343–346 (1967)
Matthäus, W., M. Sturm und E. Franke: Einige Aspekte des thermischen Regimes der Ostsee im Sommer 1975 am Beispiel der Bornholmsee. Z. Met. 26, 360–372 (1976)
Parsons, T.R., M. Takahashi and B. Hargrave: Biological oceanographic processes, 2nd ed. 332 pp. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1977
Peters, H.: GATE, CTD data measured on the F.R.G. ships, shipboard operation-calibration-editing. Ber. Inst. MeeresKde Kiel 22, 1–16 (1976)
Siedler, G. und G. Hatje: Temperatur, Salzgehalt und Dichte. In: Meereskunde der Ostsee, pp 43–60. Hrsg. von L. Magaard und G. Rheinheimer. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag 1974
Simons, T.J.: Topographic and baroclinic circulations in the Southwest Baltic. Ber. Inst. MeeresKde Kiel 25, 1–61 (1976)
Smayda, T.J.: The suspension and sinking of phytoplankton in the sea. Oceanogr. mar. biol. A. Rev. 8, 353–414 (1970)
—: Some experiments on the sinking characteristics of two freshwater diatoms. Limnol. Oceanogr. 19, 628–635 (1974)
— and B.J. Boleyn: Experimental observations on the flotation of marine diatoms. II. Skeletonema costatum and Rhizosolenia setigera. Limnol. Oceanogr. 11, 18–34 (1966)
Smetacek, V.: Die Sukzession des Phytoplanktons in der Westlichen Kieler Bucht. 151 pp. Dissertation, Universität Kiel 1975
Soutar, A., S.A. Kling, P.A. Crill, E. Duffrin and K.W. Bruland: Monitoring the marine environment through sedimentation. Nature, Lond. 266, 136–139 (1977)
Staresinic, N., G.T. Rowe, A.J. Williams III and D. Shaughnessey: Measurement of the vertical flux of particulate organic matter with a free-drifting sediment trap. Contr. Woods Hole oceanogr. Instn 3835, 1–7 (1977)
Titman, D. and P. Kilham: Sinking in freshwater phytoplankton: some ecological implications of cell nutrient status and physical mixing processes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 21, 409–417 (1976)
UNESCO: Determination of Photosynthetic pigments in sea water. Monogr. oceanogr. Methodol. (UNESCO) 1, 1–66 (1966)
Zeitzschel, B., P. Diekmann and L. Uhlmann: A new multisample sediment trap. Mar. Biol. 45, 285–288 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Hamburg
Contribution No. 185 of the Joint Research Programme 95, Kiel University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smetacek, V., von Bröckel, K., Zeitzschel, B. et al. Sedimentation of particulate matter during a phytoplankton spring bloom in relation to the hydrographical regime. Mar. Biol. 47, 211–226 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00541000
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00541000