Abstract
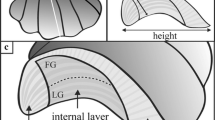
Statoliths of the short-finned squid Illex illecebrosus were chemically analyzed to define their chemical composition and surveyed by scanning electron microscope to differentiate internal structural patterns. X-ray diffraction data demonstrated that I. Illecebrosus statoliths were composed principally of CaCO3 in the aragonite crystal form. The crystals occurred in a protein matrix to form incremental patterns which radiated from the nucleus to the edge of the statoliths. The protein matrix comprised approximately 5% of the statolith by weight. The protein was principally composed of acidic amino acids. A high abundance of aspartic acid in the protein matrix indicated that the matrix would function as a template in the initiation and acceleration of the crystal growth of CaCO3. The rhythmic microstructural patterns, constructed of aragonite crystals in the protein matrix, were suggested to be daily in formation and subsequent growth estimations were in agreement with known life history information. The stable isotopic composition of the carbonate of I. illecebrosus statoliths suggested that oxygen may be deposited in isotopic equilibrium with the surrounding environment while carbon appeared to be related to biological processes. The information recorded in the statoliths as incremental growth and stable isotopic composition could provide valuable insights into the ecological history of squid.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Balch, N., T. Amaratunga and R. K. O'Dor (Eds.): Proceedings of the workshop on the squid Illex illecebrosus. Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, May, 1978; and a bibliography on the genus Illex. Fish. Mar. Ser. Tech. Rept. No. 833, 1978
Brothers, E. B., C. P. Mathews and R. Lasker: Daily growth increments in otoliths from larval and adult fishes. Fish. Bull., US 74 (1), 1–8 (1976)
Choe, S.: Daily age markings on the shell of cuttlefishes. Nature, Lond. 197, 306–307 (1963)
Clark, G. R.: Mollusk shell: daily growth lines. Science, N.Y. 161, 800–802 (1968)
Clarke, M. R.: “Growth rings” in the beaks of the squid Moroteuthis ingens (Oegopsida Onychoteuthidae). Malacologia 3, (2), 287–307 (1965)
Clarke, M. R.: The cephalopod statolith — an introduction to its form. J. mar. biol. Ass., U.K. 58, 701–712 (1978)
Clarke, M. R. and J. E. Fitch: First fossil records of cephalopod statoliths. Nature, Lond. 257, 380–381 (1975)
Carlstrom, D.: A crystallographic study of vertebrate otoliths. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 125, 441–463 (1963)
Degens, E. T., D. W. Spencer and R. H. Parker: Paleobiochemistry of molluscan shell proteins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 20, 553–579 (1967)
Degens, E. T., W. G. Deuser and R. L. Haedrich: Molecular structure and composition of fish otoliths. Mar. Biol. 2, 105–113 (1969)
Dilly, P. N.: The structure of some cephalopod statoliths. Cell. Tiss. Res. 175, 147–163 (1976)
Emiliani, C.: Isotopic paleotemperatures. Science, N.Y. 154, 851–857 (1965)
Emiliani, C.: Paleotemperature analysis of Caribbean cores. P6304-8 and P6304-9 and a generalized temperature curve for the past 425,000 years. J. Geol. 74, 109–126 (1966)
Emiliani, C., J. H. Hudson, E. A. Shinn and R. Y. George: Oxygen and carbon isotopic growth record in a reef coral from the Florida Keys and a deep sea coral from Blake Plateau. Science, N.Y. 202, 627–629 (1978)
Epstein, S. and T. Mayeda: Variations of O18 content of waters from natural sources. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 4, 213–224 (1953)
Fields, W. G.: The structure, development, food relations, reproduction, and life history of the squid, Loligo opalescens Berry, Calif. Dept. Fish and Game. Fish. Bull. U.S. 131, 1–108 (1965)
Fitch, J. E. and R. L. Brownell, Jr.: Fish otoliths in cetacean stomachs and their importance in interpreting feeding habits. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 25, 2561–2574 (1968)
Hallsworth, A. S.: Aspects of calcification. Biochem. J. 93, 255–260 (1964)
Hare, P. E.: Amino acids in the proteins from aragonite and calcite in the shells of Mytilus californianus. Science, N.Y. 139, 216–217 (1963)
Horibe, Y. and T. Oba: Temperature scales of aragonite-water and calcite-water systems. (In Japanese) Fossils 23/24, 69–79 (1972)
Hurley, G. V., P. Beck, J. Drew and R. L. Radtke: A preliminary report on validating age readings from statoliths of the short-finned squid (Illex illecebrosus). ICNAF Res. Doc. 79/II/26 (1979)
Killingley, J. S.: Migrations of California grey whales tracked by oxygen-18 variations in their epizoic barnacles. Science, N.Y. 207, 759–760 (1980)
Killingley, J. S. and W. H. Berger: Stable isotopes in a mollusk shell: detection of upwelling events. Science, N.Y. 205, 186–188 (1979)
Kristensen, T. K.: Periodical growth rings in cephalopod statoliths. Dana 1, 39–51 (1980)
Kroopnick, P.: Correlations between C13 and ΣCO2 in surface water and atmospheric CO2. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 22, 397–403 (1974)
McCrea, J. M.: On the isotopic chemistry of carbonates and a paleotemperature scale. J. chem. Phys. 18, 849–857 (1950)
Mitterer, R. M.: Amino acid composition and metal binding capability of the skeletal protein of corals. Bull. mar. Sci. 28, 173–180 (1978)
Morrow, J. E.: Preliminary keys to otoliths of some adult fishes of the Gulf of Alaska, Bering Sea and Beaufort Sea. NOAA Tech. Pap. NMFS Cir. 420, 32 pp 1979
Paine, R. T.: The measurement and application of the calorie to ecological problems. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2, 145–164 (1971)
Pannella, G.: Fish otolith: daily growth layers and periodical patterns. Science, N.Y. 174, 1124–1126 (1971)
Pannella, G. and C. MacClintock: Biological and environmental rhythms reflected in molluscan shell growth. J. Paleontol. 42, 64–89 (1968)
Radtke, R. L. and J. M. Dean: Increment formation in the otoliths of embryos, larvae and juveniles of the mummichog, Fundulus heteroclitus. Fish. Bull., U.S. 80, 201–215 (1982)
Rosenberg, A. A., K. F. Wilborg and I. M. Beck: Growth of Todarodes segittatus from the Northwest Atlantic, based on counts of statolith growth rings. Sarsia 66, 53–57 (1980)
Savin, S. M.: The history of the earth's surface temperature during the past 100 million years. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet Sci. 5, 319–355 (1977)
Scudamore, H. H.: The influence of the sinus glands upon molting and associated changes in crayfish. Physiol. Zool. 20, 187–208 (1947)
Squires, H. J.: Growth and hypothetical age of the Newfoundland bait squid, Illex illecebrosus. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 24, 1209–1217 (1967)
Spratt, J. D.: Age and growth of the market squid, Lilogo opalescens Berry, in Monterey Bay, Calif. Dept. Fish Game, Fish. Bull. 169, 35–44 (1978)
Stephens, P. R. and J. Z. Young: Semicircular canals in squids. Nature, Lond. 271, 444–445 (1978)
Summers, W. C.: Age and growth of Loligo pealei, a population study of the common Atlantic Coast squid. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 141, 189–201 (1971)
Urey, H. C., H. A. Lowenstam, S. Epstein and C. R. McKinney: Measurement of paleotemperatures and temperatures of the upper Cretaceous of England, Denmark, and the southeastern United States. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 62, 399–416 (1951)
Vinnikov, Y. A., M. Z. Aronova, T. A. Kharkeevich, T. P. Tsirulis, E. A. Lovorova and Y. V. Natochin: Structural and chemical features of the invertebrate otoliths. Z. mikrosk.-anat. Forsch., Leipzig 1, 127–140 (1981)
Weiner, S.: Aspartic acid-rich proteins: major components of the soluble organic matrix of mollusk shells. Calcif. Tiss. Res. 29, 163–167 (1979)
Weiner, S. and L. Hood: Soluble protein of the organic matrix of mollusc shells: a potential template for shell formation. Science, N.Y. 190, 987–989 (1975)
Williams, D. F., M. A. Sommer and M. L. Bender: Carbon isotopic compositions of recent planktonic foraminifera of the Indian Ocean. Earth Planet Sci. Letters 36, 391–403 (1977)
Wells, J. W.: Coral growth and geochronometry. Nature, Lond. 197, 948–950 (1963)
Yagi, T.: On the growth of the shell in Sepia esculenta (Hoyle) caught in Tokyo Bay. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 26, 640–645 (1960)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by S. K. Pierce, College Park
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radtke, R.L. Chemical and structural characteristics of statoliths from the short-finned squid Illex illecebrosus . Marine Biology 76, 47–54 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393054
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393054