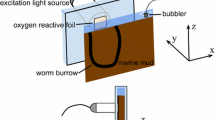
Abstract
O2-flux into sediments attributed to the pumping behaviour of two macrofauna species, Callianassa subterranea (Decapoda) and Lanice conchilega (Polychaeta) was investigated. Samples were obtained from the North Sea near Helgoland in 1989 and 1990. The two species were found to transport roughly similar amounts (3 mmolm-2d-1) of oxygen into the sediment although they displayed markedly different pumping behaviours. Irrigation by C. subterranea was intermittent and characterized by regularly recurring breathing currents which lasted 2.6 min and were separated by 40-min pauses. In addition to this regular intermittent irrigation, an irregular mode was observed. C. subterranea constructed a complex burrow system. At least half of the burrow wall was not in contact with oxygenated water, however, and thus not effective as additional interface for O2-exchange. Sediment expelled from the burrow increased the total oxygen uptake (TOU) relative to the surrounding sediment surface. L. conchilega moved water much more frequently (every 4 min) than C. subterranea. We suggest that L. conchilega acted as a piston when moving in its tube, exchanging burrow water with the overlying water. This mechanism, termed ‘piston-pumping’, is also potentially important in other smaller tube dwelling organisms. At a shallow water station in the southern North Sea 21 ind of C. subterranea constructed 1.6 m2 burrow surface per m2. L. conchilega (300 ind m-2) created only 0.37 m2m-2 tube surface. On the basis of the abundance and oxygen transport associated with pumping activity, it is calculated that the two species increase TOU by 85% compared to O2-flux across the sediment-water interface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adema FPHM, Creutzberg F, Noort GJV (1982) Notes on the occurrence of some poorly known Decapoda (Crustacea) in the southern North Sea. Zool Bijdragen 28: 9–32
Aller RC (1982) The effects of macrobenthos on chemical properties of marine sediment and overlying water. In: McCall PL, Tevesz MJS (eds) Animal-sediment relations. Plenum Press, New York, pp 53–104
Aller RC, Aller JY (1992) Meiofauna and solute transport in marine muds. Limnol Oceanogr 37: 1018–1033
Anderson JG, Meadows PS (1978) Microenvironments in marine sediments. Proc R Soc Edinb 76 B: 1–16
Archer D, Devol A (1992) Benthic O2-fluxes on the Washington shelf and slope: a comparison of in situ microelectrode and chamber flux measurements. Limnol Oceanogr 37: 614–629
Atkinson RJA, Nash RDM (1990) Some preliminary observations on the burrow of Callianassa subterranea (Montague) (Decapoda: Thalassinidea) from the west coast of Scotland. J nat Hist 24: 403–413
Balzer W, Erlenkeuser H, Hartman M, Müller PJ, Pollehne F (1987) Diagenesis and exchange processes at the benthic boundary. In: Ruhmor J, Walger E, Zeitschel B (eds) Seawater-sediment interactions in coastal waters — an interdisciplinary approach. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 111–161
Berner RA (1980) Early diagenesis. A theoretical approach. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Broecker WS, Peng T-H (1974) Gas exchange rates between air and sea. Tellus 26: 21–35
Boudreau BP (1984) On the equivalence of non-local and radial diffusion models for porewater irrigation. J mar Res 42: 731–735
Buhr K-J (1976) Suspension-feeding and assimilation efficiency in Lanice conchilega (Polychaeta). Mar Biol 38: 373–383
Buhr K-J, Winter JE (1977) Distribution and maintenance of a Lanice conchilega association in the Weser Estuary (FRG), with special reference to the suspension feeding behaviour of Lanice conchilega. In: Keegan BE, Ceidigh PO, Boaden PJS (eds) Proc 11th Eur mar Biol Symp, Galway, Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 101–113
Christensen JP, Devol AH, Smethie Jr WM (1984) Biological enhancement of solute exchange between sediments and bottom water of the Washington continental shelf. Contin Shelf Res 3: 9–23
Cramer A (1989) A common artefact in estimates of benthic community respiration caused by the use of stainless steel. Neth J Sea Res 23: 1–6
deWilde PAWJ, Berghuis EM, Kok A (1984) Structure and energy demand of the benthic community of the Oyster Ground, central North Sea. Neth J Sea Res 18: 143–159
deWilde PAWJ, Berghuis EM, Kok A (1986) Biomass and activity of benthic fauna on the Fladden Ground (northern North Sea). Neth J Sea Res 20: 313–323
Duineveld GCA, Künitzer A, Niermann U, deWilde PAJ, Gray JS (1991) The macrobenthos of the North Sea. Neth J Sea Res 28: 53–65
Dworschak PC (1981) The pumping rates of the burrowing shrimp Upogebia pusilla (PETAGNA) (Decapoda, Thalassinidea). J exp mar Biol Ecol 52: 25–35
Dworschak PC (1983) The biology of Upogebia pusilla (PETAGNA) (Decapoda, Thalassinidea) I. The burrows. Mar Ecol Naples 4: 19–43
Forster S (1991) Die Bedeutung biogener Strukturen für den Sauerstoffluß ins Sediment. Ph.D. thesis, CA Universität, Kiel
Forster S, Graf G (1992) Continuously measured changes in redox potential influenced by oxygen penetrating from burrows of Callianassa subterranea. Hydrobiologia 235/236: 527–532
Glud RN, Gundersen JK, Jørgensen BB, Revsbech NP, Schulz HD (1994) Diffusive and total oxygen uptake of deep-sea sediments in the eastern South Atlantic Ocean: in situ and laboratory measurements. Deep-Sea Res 41: 1767–1788
Gerlach SA, Hahn AE, Schrage M (1985) Size spectra of benthic biomass and metabolism. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 26: 161–173
Griffis RB, Suchanek TH (1991) A model of burrow architecture and trophic modes in thalassinidean shrimp (Decapoda: Thalassinidea) Mar Ecol Prog Ser 79: 171–183
Gust G, Harrison TJ (1981) Biological pumps at the sediment-water interface: mechanistic evaluation of the alpheid shrimp Alpheus mackayi and its irrigation pattern. Mar Biol 64: 71–78
Hickel W, Bauerfeind E, Niermann U, Westernhagen Hv (1989) Oxygen deficiency in the south-eastern North Sea: sources and biological effects. Ber biol Anst Helgoland 4: 1–148
Jørgensen CB (1975) Comparative physiology of suspension feeding. A Rev Physiol 30: 391–454
Jørgensen BB, Des Marais DJ (1990) The diffusive boundary layer of sediments: oxygen microgradients over a microbial mat. Limnol Oceanogr 35: 1343–1355
Kitlar J (1991) Der Einfluß der Bioturbation auf den Transport gelöster Stoffe im Porenwasser. Ph.D. thesis, CA Universität, Kiel
Kristensen E (1983a) Comparison of polychaete (Nereis spp.) ventilation in plastic tubes and natural sediment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 12: 307–309
Kristensen E (1983b) Ventilation and oxygen uptake by three species of Nereis (Annelida: Polychaeta). II. Effects of temperature and salinity changes. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 12: 299–306
LaBarbera M, Vogel S (1976) An inexpensive thermistor flowmeter for aquatic biology. Limnol Oceanogr 21: 750–756
Lee H, Swartz RC (1980) Biological processes affecting the distribution of pollutants in marine sediments. Part II. Biodeposition and bioturbation. Contaminants and sediments. Ann Arbor Scientific Publications, Ann Arbor, Michigan, pp 555–606
Li Y-H, Gregory S (1974) Diffusion of ions in sea water and in deep-sea sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 38: 703–714
Lindeboom HJ, Sandee AJJ, deKlerk-van der Driessche HAJ (1985) A new bell jar/microelectrode method to measure changing oxygen fluxes in illuminated sediments with a microbial cover. Limnol Oceanogr 30: 693–698
Lutze J (1938) Über Systematik, Entwicklung und Ökologie von Callianassa subterranea. Helgolander wiss Meeresunters 1: 162–199
Östlund P, Hallberg RO, Hallstadius L (1990) Pore water mixing by microorganisms, monitored by a radiotracer method. Geomicrobiol J 7: 253–264
Pamatmat MM (1971) Oxygen consumption by the sea bed. IV. Shipboard and laboratory experiments. Limnol Oceanogr 16: 536–550
Powilleit M (1991) CO2-Messungen zur Untersuchung des anaeroben Stoffwechsels benthischer Evertebraten und zur Aktivitätsbestimmung der gesamten Sediment-Lebensgemeinschaft. Ph.D. thesis, CA Universität, Kiel
Pritchard AW, Eddy S (1979) Lactate formation in Callianassa californiensis and Upogebia pugettensis (Crustacea: Thalassinidea). Mar Biol 50: 249–253
Reise K (1985) Tidal flat ecology. Ecological studies, analysis and synthesis. Springer, Heidelberg
Revsbech NP, Jørgensen BB, Blackburn TH (1980) Oxygen in the sea bottom measured with a microelectrode. Science, NY 207: 1355–1356
Revsbech NP, Ward DM (1983) Oxygen microelectrode that is insensitive to medium chemical composition: use in acid microbial mat dominated by Cyanidium caldarium. Appl envir Microbiol 45: 755–759
Riisgård HU (1991) On suspension feeding in the polychaete Nereis diversicolor. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 70: 29–37
Roberts HH, Wiseman Jr WJ Suchanek T (1981) Lagoon sediment transport: the significant effect of Callianasa bioturbation. In: Gomez ED et al. (eds) Proc 4th int coral Reef Symp, Marine Sciences Center, University of the Phillipines, Manilag pp 459–465
Rutgers van der Loeff MM, Anderson LG, Hall POJ, Iverfeldt A, Josefson AB, Sundby B, Westerlund SFG (1984) The asphyxation technique: an approach to distinguishing between molecular diffusion and biologically mediated water transport at the sediment-water interface. Limnol Oceanogr 29: 675–686
Salzwedel H, Rachor E, Gerdes D (1985) Benthic macrofauna communities in the German Bight. Veröff Inst Meeresforsch Bremerh 20: 199–267
Seilacher A (1951) Der Röhrenbau von Lanice conchilega (Polychaeta). Ein Beitrag zur Deutung fossiler Lebensspuren. Senckenbergia 32: 267–280
Smith CR, Jumars PA, DeMaster DJ (1986) In situ studies of megafaunal mounds indicate rapid sediment turnover and community response at the deep-sea floor. Nature, Lond 323: 251–253
Stripp K (1969) Das Verhältnis von Makrofauna und Meiofauna in den Sedimenten des Helgoländer Bucht. Veröff Inst Meeresforsch Bremerh 12: 143–148
Suchanek T (1985) Thalassinid shrimp burrows: ecological significance of the species-specific architecture. In: Gabriéc et al. (eds) Proc 5th int coral Reef Congr, Antenne Museum-EPHE, Moorea, French Polynesia, pp 205–210
Vogel S (1981) Life in moving fluid. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Wheatcroft RA, Jumars PJ, Smith CR, Nowell ARM (1990) A mechanistic view of the particulate bioturbation coefficient: step length, rest periods and transport directions. J mar Res 48: 177–207
Witbaard R, Duineveld GCA (1989) Some aspects of the biology and ecology of the burrowing shrimp Callianassa subterranea (Montagu) (Thalassinidea) from the southern North Sea. Sarsia 74: 209–219
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forster, S., Graf, G. Impact of irrigation on oxygen flux into the sediment: intermittent pumping by Callianassa subterranea and “piston-pumping” by Lanice conchilega . Marine Biology 123, 335–346 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00353625
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00353625