Abstract
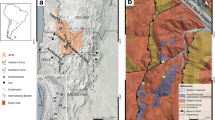
The ophiolitic mélange in the uppermost tectonic unit of the Cretan nappe pile contains crystalline slices which consist of a low-pressure/high-temperature metamorphic sequence and synmetamorphic intrusions, ranging in composition from diorite to granite. The plutonic rocks conform to two different igneous suites, dominated by diorites in eastern, and granites in central Crete, displaying I-type and A-type characters, respectively. Some of the granites from central Crete are classified as transitional I/S-type. They are closely associated with migmatitic paragneisses. Based on major and trace element, REE, Sr- and Nd-isotope geochemistry, the mafic members of both suites are derived from a depleted mantle source. The higher concentrations of P and Ti in the mafic members of the igneous suite in central Crete and the deviant trend of the whole suite may be explained by a different mantle source or a lower degree of partial melting. In both suites, magmatic evolution was governed by fractional crystallization of amphibole/clinopyroxene, plagioclase and minor phases. In addition, mixing or mingling of compositionally different magmas is indicated for the intrusive suite of eastern Crete whereas in central Crete the magma composition was at least partially modified through assimilation of (meta)pelites. The geochemical results suggest that the plutonic rocks formed in a supra-subduction zone setting. However, a formation during continental lithospheric extension cannot be ruled out. Published and new Rb–Sr and K–Ar dates on amphiboles and biotites from intrusive rocks and their metamorphic country rocks show that the peak of the low-P/high-T metamorphism and the intrusion of the two igneous suites testify to the same thermal event of Late Cretaceous age. A similar Late Cretaceous association of metamorphic and plutonic rocks has been described from the uppermost tectonic unit in the Attic–Cycladic Crystalline Complex. Together with the Cretan occurrences, they form a small sector radiating SSW along a distance of 300 km, across the general trend of the tectonic zones in the Hellenic orogen. This N–S alignment is regarded as a primary feature which may delineate the frontier zone between the Hellenides and the Taurides. The real paleogeographic position and geodynamic significance of the Late Cretaceous low-pressure/high-temperature belt, however, remains enigmatic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 June 1999 / Accepted: 2 February 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Langosch, A., Seidel, E., Stosch, HG. et al. Intrusive rocks in the ophiolitic mélange of Crete – Witnesses to a Late Cretaceous thermal event of enigmatic geological position. Contrib Mineral Petrol 139, 339–355 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100000136
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100000136