Abstract
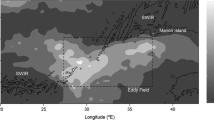
The at-sea behaviour of marine top predators provides valuable insights into the distribution of prey species and strategies used by predators to exploit patchily distributed resources. We describe the water column usage and dive strategies of female southern elephant seals from Marion Island tracked between 2004 and 2008. Dives representing increases in forage effort were identified using a method that combines dive type analyses and the calculation of relative amounts of time that animals spend in the bottom phases of dives. Results from this analysis indicate that female elephant seals from Marion Island tend to display lower levels of forage effort closer to the island and display intensive opportunistic forage bouts that occur at a minimum distance of approximately 215 km from the island. Females from Marion Island dived deeper and for longer periods of time, compared to females from other populations. Most animals displayed positive diel vertical migration, evidently foraging pelagically on vertically migrating prey. A few animals displayed periods of reverse (negative) diel vertical migration, however, diving to deeper depths at night, compared to daytime. This behaviour is difficult to explain and prey species targeted during such periods unknown. Our results illustrate plasticity in foraging behaviour of southern elephant seals, as well as inter-population differences in forage strategies.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argos (1996) Argos user’s manual. Collecte localisation satellites (CLS)
Bailleul F, Charrassin J-B, Ezraty R, Girard-Ardhuin F, McMahon CR, Field IC, Guinet C (2007a) Southern elephant seals from Kerguelen Islands confronted by Antarctic Sea ice. Changes in movements and in diving behaviour. Deep Sea Res Part II: Topical Stud Oceanogr 54:343–355
Bailleul F, Charrassin J-B, Monestiez P, Roquet F, Biuw M, Guinet C (2007b) Successful foraging zones of southern elephant seals from the Kerguelen Islands in relation to oceanographic conditions. Philos Transact Royal Soc B 362:2169–2181
Bailleul F, Pinaud D, Hindell M, Charrassin J-B, Guinet C (2008) Assessment of scale-dependent foraging behaviour in southern elephant seals incorporating the vertical dimension: a development of the first passage time method. J Anim Ecol 77:948–957
Belkin IM, Gordon AL (1996) Southern Ocean fronts from the Greenwich meridian to Tasmania. J Geophys Res 101:3675–3696
Bennet KA, McConnell BJ, Fedak M (2001) Diurnal and seasonal variations in the duration and depth of the longest dives in southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina): possible physiological and behavioural constraints. J Exp Biol 204:649–662
Bester MN (1988a) Chemical restraint of Antarctic fur seals and southern elephant seals. South African J Wildlife Res 18:57–60
Bester MN (1988b) Marking and monitoring studies of the Kerguelen stock of southern elephant seals Mirounga leonina and their bearing on biological research in the Vestfold Hills. Hydrobiologia 165:269–277
Bester MN, Pansegrouw HM (1992) Ranging behaviour of southern elephant seal cows from Marion Island. South African J Sci 88:574–575
Bestley S, Patterson TA, Hindell MA, Gunn JS (2010) Predicting feeding success in a migratory predator: integrating telemetry, environment, and modeling techniques. Ecology 91:2373–2384
Biuw M, McConnell BJ, Bradshaw CJA, Burton HR, Fedak M (2003) Blubber and buoyancy: monitoring the body condition of free-ranging seals using simple dive characteristics. J Exp Biol 206:3405–3423
Biuw M, Boehme L, Guinet C, Hindell MA, Costa DP, Charrassin J-B, Roquet F, Bailleul F, Meredith M, Thorpe S, Tremblay Y, McDonald BI, Park Y-H, Rintoul SR, Bindoff N, Goebel ME, Crocker DE, Lovell P, Nicholson J, Monks F, Fedak M (2007) Variations in behavior and condition of a Southern Ocean top predator in relation to in situ oceanographic conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:13705–13710
Biuw M, Nøst OA, Stien A, Zhou Q, Lydersen C, Kovacs KM (2010) Effects of hydrographic variability on the spatial, seasonal and diel diving patterns of southern elephant seals in the eastern Weddell Sea. PLoS ONE 5:e13816
Boehme L, Lovell P, Biuw M, Roquet F, Nicholson J, Thorpe SE, Meredith MP, Fedak M (2009) Technical Note: Animal-borne CTD-satellite relay data loggers for real-time oceanographic data collection. Ocean Sci 5:685–695
Boyd IL, Arnbom T (1991) Diving behaviour in relation to water temperature in the southern elephant seal: foraging implications. Polar Biol 11:259–266
Bradshaw CJA, Hindell MA, Best NJ, Philip KL, Wilson G, Nichols PD (2003) You are what you eat: describing the foraging ecology of southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) using blubber fatty acids. Proc Royal Soc B 270:1283–1292
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32
Burns JM, Hindell MA, Bradshaw CJA, Costa DP (2008) Fine-scale habitat selection of crabeater seals as determined by diving behavior. Deep-Sea Res II 55:500–514
Campagna C, Le Boeuf BJ, Blackwell SB, Crocker DE, Quintana F (1995) Diving behaviour and foraging location of female southern elephant seals from Patagonia. J Zool, London 236:55–71
Campagna C, Piola AR, Rosa Marin M, Lewis M, Zajaczkovski U, Fernandez T (2007) Deep divers in shallow seas: southern elephant seals on the Patagonian shelf. Deep-Sea Res I 54:1792–1814
Carlini AR, Daneri GA, Marquez MEI, Bornemann H, Panarello HO, Casaux R, Ramdohr S, Plötz J (2005) Food consumption estimates of southern elephant seal females during their post-breeding aquatic phase at King George Island. Polar Biol 28:769–775
Collins MA, Rodhouse PGK (2006) Southern Ocean cephalopods. Adv Marine Biol 50:191–265
Collins MA, Xavier JC, Johnston NM, North AW, Enderlein P, Tarling GA, Waluda CM, Hawker EJ, Cunningham NJ (2008) Patterns in the distribution of myctophid fish in the northern Scotia Sea ecosystem. Polar Biol 31:837–851
de Bruyn PJN (2009) Life history studies of the southern elephant seal population at Marion Island. Ph.D. thesis. University of Pretoria
de Bruyn PJN, Tosh CA, Oosthuizen WC, Phalanndwa MV, Bester MN (2008) Temporary marking of unweaned southern elephant seal (Mirounga leonina L.) pups. South African J Wildlife Res 38:133–137
Fauchald P, Tveraa T (2003) Using first-passage time in the analysis of area-restricted search and habitat selection. Ecology 84:282–288
Fedak M, Lovell P, Grant SM (2001) Two approaches to compressing and interpreting time-depth information and satellite-linked data recorders as collected by time-depth recorders. Marine Mammal Sci 17:94–110
Field I, Hindell MA, Slip D, Michael KJ (2001) Foraging strategies of southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) in relation to frontal zones and water masses. Antarct Sci 13:371–379
Freitas C, Lydersen C, Fedak M, Kovacs KM (2008) A simple new algorithm to filter marine mammal Argos locations. Marine Mammal Sci 24:315–325
Gende SM, Sigler MF (2006) Persistence of forage fish ‘hot spots’ and its association with foraging Steller sea lions (Eumetopias jubatus) in southeast Alaska. Deep-Sea Res II 53:432–441
Hays GC (2003) A review of the adaptive significance and ecosystem consequences of zooplankton diel vertical migrations. Hydrobiologia 503:163–170
Hindell MA, McMahon C (2000) Long distance movement of a southern elephant seal (Mirounga leonina) from Macquarie Island to Peter 1 Øy. Marine Mammal Sci 16:504–507
Hindell MA, Slip DJ, Burton HR (1991) The diving behaviour of adult male and female southern elephant seals, Mirounga leonina (Pinnipedia: Phocidae). Australian J Zool 39:595–619
Hindell MA, Lea M-A, Morrice MG, McMahon CR (2000) Metabolic limits on dive duration and swimming speed in the southern elephant seal Mirounga leonina. Physiol Biochem Zool 73:790–798
IOC, IHO, BODC (2003) Centenary Edition of the GEBCO Digital Atlas, published on CD-ROM on behalf of the Intergovernmental oceanographic commission and the international hydrographic organization as part of the general Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans; British oceanographic data centre, Liverpool
Jonker FC (1997) Ranging and diving behaviour of adult female southern elephant seals from Marion Island. M.Sc. dissertation. University of Pretoria
Jonker FC, Bester MN (1994) The diving behaviour of adult southern elephant seal, Mirounga leonina, cows from Marion Island. South African J Antarctic Res 24:75–93
Jonker FC, Bester MN (1998) Seasonal movements and foraging areas of adult southern female elephant seals, Mirounga leonina, from Marion Island. Antarct Sci 10:21–30
Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (1994) Elephant seals: population ecology, behavior, and physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley
Le Boeuf BJ, Crocker DE, Costa DP, Blackwell SB, Webb PM, Houser DS (2000) Foraging ecology of northern elephant seals. Ecol Monogr 70:353–382
Lewin-Koh NJ, Bivand R (2008) The maptools package
Liaw A, Wiener M (2002) Classification and regression by randomForest R News, pp 18–22
McConnell BJ, Chambers C, Fedak MA (1992) Foraging ecology of southern elephant seals in relation to the bathymetry and productivity of the Southern Ocean. Antarct Sci 4:393–398
McConnell BJ, Fedak M, Burton HR, Engelhard GH, Reijnders PJH (2002) Movements and foraging areas of naïve, recently weaned southern elephant seal pups. J Anim Ecol 71:65–78
McIntyre T, de Bruyn PJN, Ansorge IJ, Bester MN, Bornemann H, Plötz J, Tosh CA (2010a) A lifetime at depth: vertical distribution of southern elephant seals in the water column. Polar Biol 33:1037–1048
McIntyre T, Tosh CA, Plötz J, Bornemann H, Bester MN (2010b) Segregation in a sexually dimorphic mammal: a mixed-effects modelling analysis of diving behaviour in southern elephant seals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 412:293–304
McMahon CR, Bester MN, Burton HR, Hindell MA, Bradshaw CJA (2005) Population status, trends and a re-examination of the hypotheses explaining the recent declines of the southern elephant seal Mirounga leonina. Mammal Rev 35:82–100
Mitani Y, Andrews RD, Sato K, Kato A, Naito Y, Costa DP (2009) Three-dimensional resting behaviour of northern elephant seals: drifting like a falling leaf. Biol Lett 6:163–166
Patterson TA, Thomas L, Wilcox C, Ovaskainen O, Matthiopoulos J (2008) State–space models of individual animal movement. Trends Ecol Evol 23:87–94
Patterson TA, Basson M, Bravington MV, Gunn JS (2009) Classifying movement behaviour in relation to environmental conditions using hidden Markov models. J Anim Ecol 78:1113–1123
Photopoulos T (2007) Behavioural changes of a long-ranging diver in response to oceanographic conditions. M.Sc. thesis, University of St Andrews
Pistorius PA, Bester MN, Kirkman SP (1999) Survivorship of a declining population of southern elephant seals, Mirounga leonina, in relation to age, sex and cohort. Oecologia 121:210–211
Pistorius PA, Bester MN, Kirkman SP, Taylor FE (2001) Temporal changes in fecundity and age at sexual maturity of southern elephant seals at Marion Island. Polar Biol 24:343–348
Pistorius PA, Bester MN, Lewis MN, Taylor FE, Campagna C, Kirkman SP (2004) Adult female survival, population trend, and the implications of early primiparity in a capital breeder, the southern elephant seal (Mirounga leonina). J Zool, London 263:107–119
Pistorius PA, Bester MN, Hofmeyr GJG, Kirkman SP, Taylor FE (2008a) Seasonal survival and the relative cost of first reproduction in adult female southern elephant seals. J Mammal 89:567–574
Pistorius PA, Taylor FE, Bester MN, Hofmeyr GJG, Kirkman SP (2008b) Evidence for density dependent population regulation in southern elephant seals in the southern Indian Ocean. African Zool 43:75–80
R Development Core Team (2008) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for statistical computing, Vienna, Austria
Rintoul SR, Donguy JR, Roemmich DH (1997) Seasonal evolution of upper ocean thermal structure between Tasmania and Antarctica. Deep-Sea Res I 44:1185–1202
Robinson PW, Tremblay Y, Crocker DE, Kappes MA, Kuhn CE, Shaffer SA, Simmons SE, Costa DP (2007) A comparison of indirect measures of feeding behaviour based on ARGOS tracking data. Deep-Sea Res II 54:356–368
Robinson PW, Simmons SE, Crocker DE, Costa DP (2010) Measurements of foraging success in a highly pelagic marine predator, the northern elephant seal. J Anim Ecol 79:1146–1156
Rodhouse PG, White MG (1995) Cephalopods occupy the ecological niche of epipelagic fish in the Antarctic Polar Frontal Zone. Biol Bull 189:77–80
Schreer JF, Kovacs KM, O’Hara Hines RJ (2001) Comparative diving patterns of pinnipeds and seabirds. Ecol Monogr 71:137–162
Scott BE, Sharples J, Ross ON, Wang J, Pierce GJ, Camphuysen CJ (2010) Sub-surface hotspots in shallow seas: fine-scale limited locations of top predator foraging habitat indicated by tidal mixing and sub-surface chlorophyll. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 408:207–226
Slip DJ, Hindell MA, Burton HR (1994) Diving behavior of southern elephant seals from Macquarie Island: an overview. In: Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (eds) Elephant seals: population ecology, behavior, and physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 253–270
Smetacek V, Nicol S (2005) Polar ocean ecosystems in a changing world. Nature 437:362–368
Sydeman WJ, Brodeur RD, Grimes CB, Bychkov AS, McKinnell S (2006) Marine habitat ‘‘hotspots’’ and their use by migratory species and top predators in the North Pacific Ocean: introduction. Deep-Sea Res II 53:247–249
Tosh CA (2010) Oceanographic signatures and foraging areas of southern elephant seals. Ph.D. thesis. University of Pretoria
Tosh CA, Bornemann H, Ramdohr S, Schröder M, Martin T, Carlini A, Plötz J, Bester MN (2009) Adult male southern elephant seals from King George Island utilize the Weddell Sea. Antarct Sci 21:113–121
Tremblay Y, Roberts AJ, Costa DP (2007) Fractal landscape method: an alternative approach to measuring area-restricted searching behavior. J Exp Biol 210:935–945
Worton BJ (1989) Kernel methods for estimating the utilization distribution in home-range studies. Ecology 70:164–168
Acknowledgments
We thank Nico de Buyn, Chris Oosthuizen, Mashudu Phalanndwa, Ryan Reisinger, Thomas Mufanadzo, Phathu Radzilani, Brent Stewart and Greg Hofmeyr for assistance in the field with the deployment of satellite tags. Martin Biuw generously provided R codes (and helpful assistance) for the dive classifications and the use of the maptools package. Comments from three anonymous reviewers on a previous version of this manuscript were very constructive and greatly improved it. The Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research (Germany), the Department of Science and Technology through the National Research Foundation (South Africa) and the South African National Antarctic Programme provided financial and logistical support. Much of this research was carried out under the South Africa/Germany part of the project MEOP (Marine Mammals Exploring the Oceans Pole to Pole), carried out as part of the International Polar Year.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by U. Siebert.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McIntyre, T., Bornemann, H., Plötz, J. et al. Water column use and forage strategies of female southern elephant seals from Marion Island. Mar Biol 158, 2125–2139 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-011-1719-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-011-1719-2